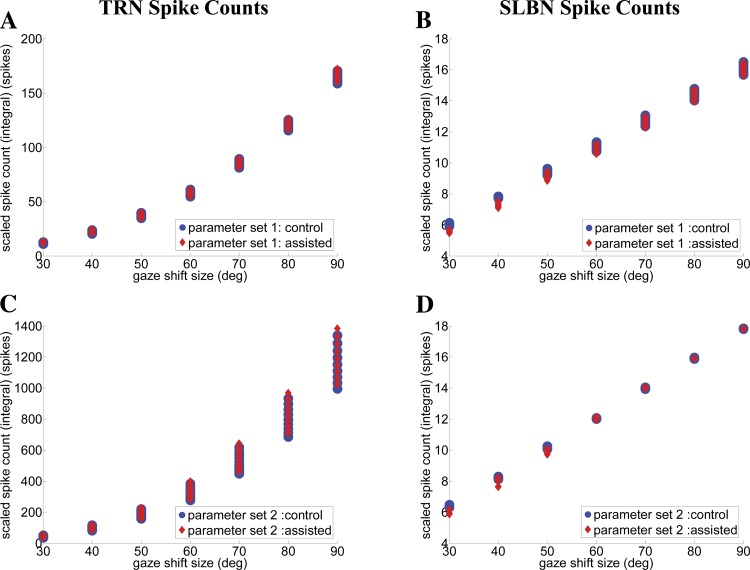
Fig. 12.
Burst neuron spike counts for gaze shifts with and without long-duration assisting head perturbations. A and C: TRN. B and D: SLBN. A and C describe counts with parameter set 1 (default) providing single-peak gaze velocities; B and D use parameter set 2 for double-peak gaze velocities. Results are consistent with reports on TRN cells (Goossens and Van Opstal 2006) and SLBN cells (Cullen et al. 1993), particularly the stronger linear relation of SLBN spike counts with gaze shift size compared with TRN results. The shapes of these curves are not affected by the presence of assisting perturbations (red dots) of the type used in Fig. 7, a model prediction.