Figure 6.
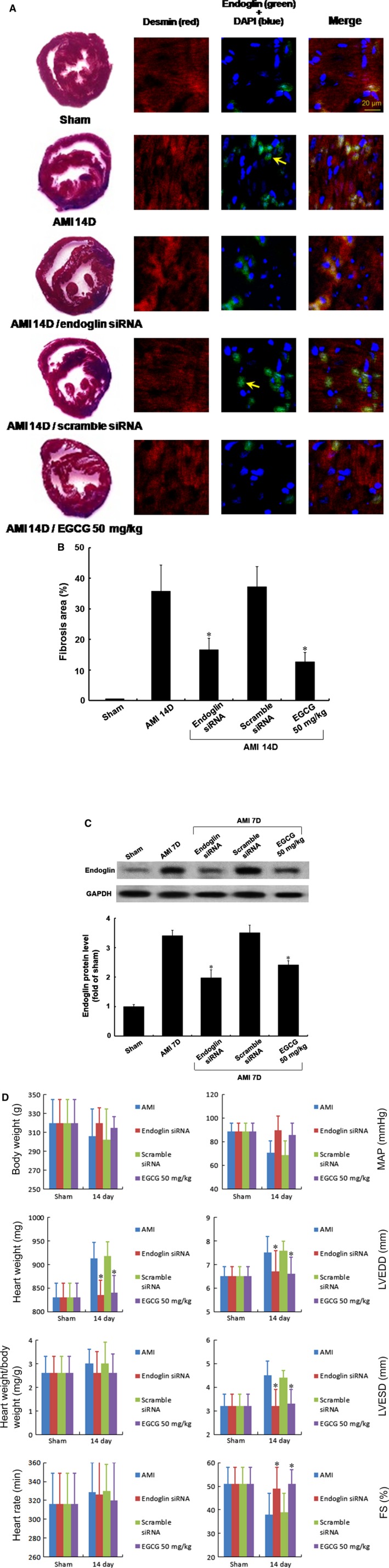
Immunohistochemnical staining of the left ventricular myocardium after induction of acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and hemodynamic monitor by treatment with/without EGCG or endoglin siRNA. Significantly increased immunoreactive signals were observed for endoglin following AMI for 14 days. (A) Left panel, representative cross‐section of the cardiac ventricle stained with the haematoxylin by EGCG (50 mg/kg) treatment or endoglin siRNA. The right three panels showed double staining for endoglin siRNA (green colour) by fibroblasts actin labelling (red colour). (B) Quantitative analysis of the cross‐sectional area of the endoglin protein expression after AMI for 14 days. (C) Quantitative analysis of the cross‐sectional myocardial fibrosis size measured, EGCG and endoglin siRNA significantly decreased the myocardial fibrosis induced following AMI for 7 days. Rare endoglin signals were observed in the sham group. (D) EGCG and endoglin siRNA attenuated the heart weight, the left ventricular end‐diastolic dimension (LVEDD), the left ventricular systolic–diastolic dimension (LVESD) and the fraction shortening (FS). P < 0.05 versus control. EGCG, epigallocatechin‐3‐O‐gallate.
