Fig. 5.
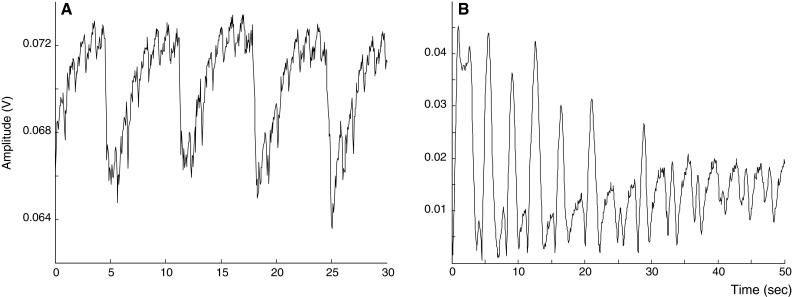
Potential features of the frequency modulated continuous wave radar. a Example (patient number 8) of five breaths with 31 superimposed heartbeats on the 30 s radar signal during mechanical ventilation, that correspond to the heart rate measured by pulse oximetry. b Example (patient number 1) of a radar trace during 50 s of spontaneous breathing with different breathing patterns potentially corresponding to the tidal volumes. Every inspiratory cycle is characterized by a first peak (chest wall expansion during inhalation), followed by a more smoothed peak (during exhalation). We presume that larger tidal volumes, thus increased chest wall expansion result in higher amplitudes of the echoed radar waves
