Figure 3. Xvelo self-assembly is dependent on its prion-like domain.
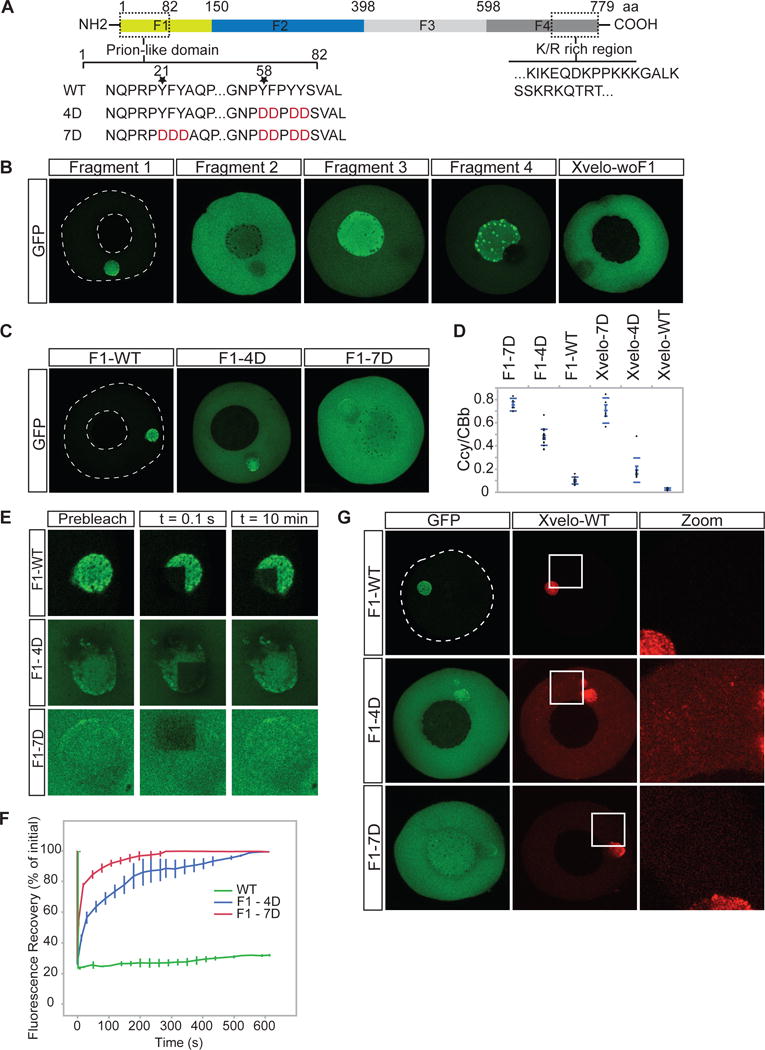
(A) Diagram of the known structural elements of Xvelo. Prion-like domain, mutants (4D and 7D) and the fragments of Xvelo (F1 to F4) are marked in the figure.
(B) mRNAs encoding for Xvelo fragments shown in (A) and Xvelo without fragment 1 (Xvelo-woF1) are in vitro synthesized and micro-injected into stage I oocytes. Oocytes were imaged after overnight incubation in Oocyte Culture Medium (OCM).
(C) mRNAs encoding for wild type and PLD mutants of Fragment1-GFP were microinjected into oocytes. Oocytes were incubated overnight and imaged.
(D) Ratio of GFP concentration in the oocyte cytoplasm (Ccy) to the Balbiani body (CBb) in oocytes injected with mRNAs encoding for indicated proteins. Relative concentrations were calculated by using oocyte or the Balbiani body volume from z-stacks and the fluorescent intensity of GFP. Mean values and standard errors of 10 oocytes are plotted.
(E) Internal rearrangement of fluorescent wild-type or mutant F1-GFP particles after photobleaching over time.
(F) The fluorescent recovery of photobleached wild-type or mutant F1-GFP in Balbiani bodies in (E) and two other biological replicates for each are shown by quantification of fluorescence in bleached region over time normalized by an unbleached neighbouring region.
(G) mRNAs encoding for full length Xvelo-mCherry wild-type, and GFP tagged fragments, F1-WT-GFP, F1-4D-GFP and F1-7D-GFP, were in vitro synthesized. F1-WT-GFP or mutants were mixed with equal amounts of full length Xvelo-mCherry mRNA and microinjected into the oocytes. After overnight incubation, the oocytes were imaged by scanning confocal microscopy.
See also Figure S3
