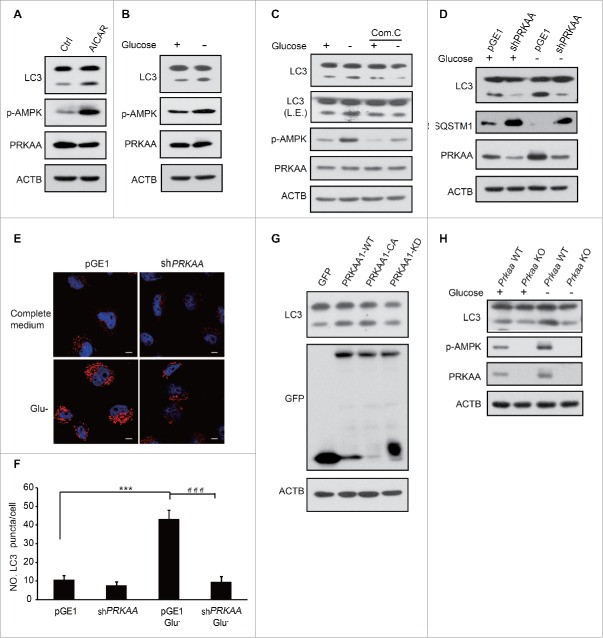
Figure 1.
AMPK is essential for the induction of autophagy. HEK293T cells were treated with 0.25 mM AICAR for 1 h (A) or subjected to glucose deprivation for 3 h (B). Autophagy was determined by LC3 immunoblotting. p-AMPK was determined indicating AMPK activation. (C) After pretreatment with 10 μM compound C for 0.5 h, glucose starvation was performed in HEK293T cells for 3 h. LC3 and AMPK activity were then assayed using immunoblotting. (D) HEK293T cells were transfected with pGE1-shPRKAA and grown under nutrient-rich conditions for 36 h before being lysed for western blotting. LC3 and PRKAA were detected by immunoblotting. (E) Representative images of cells were fixed and examined by immunofluorescence after transfection with pGE1-shPRKAA in HeLa cells for 48 h, and glucose starvation (3 h). The red dots are LC3 puncta. Scale bars: 10 μm. (F) Quantification of GFP-LC3 puncta shown in (E). Bars are mean ± SEM of triplicate samples (≥ 10 cells analyzed per sample). The comparison of different groups was carried out using 2-tailed unpaired Student t test by Graphpad Prism5 (Graphpad Software, San Diego, CA, USA). Differences were considered statistically significant (***, ###) at P < 0.05. (G) GFP-PRKAA1 WT, CA and KD were transfected into HEK293T cells to examine the role of AMPK in autophagy. (H) Prkaa WT and KO MEF cells were subjected to glucose starvation for 3 h. Cell lysates were probed with the indicated antibodies.