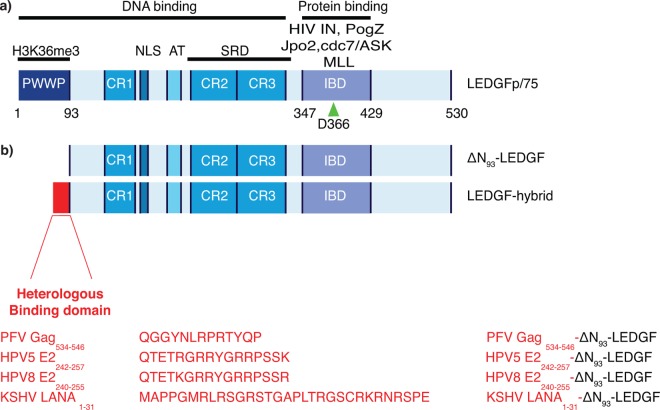
Fig 1. Schematic representation of the LEDGF/p75 domain structure and artificial LEDGF-hybrids.
(a) LEDGF/p75 contains a C-terminal protein-binding domain, coined Integrase Binding Domain (IBD) responsible for HIV-IN interaction. Several endogenous proteins like Jpo2, PogZ and MLL bind to the same interface. At its N-terminal end carries multiple chromatin interacting domains, the PWWP domain, the AT hook-like domain (AT) and three charged regions (CR1, 2, 3). D366 is a pivotal amino acid involved in HIV-IN interaction (arrowhead). Mutation to Asn (D366N) abolishes HIV-IN interaction. The lower panel (b) depicts the different LEDGF-hybrids, PFV Gag534-546-ΔN93-LEDGF, HPV5 E2242-257-ΔN93-LEDGF, HPV8 E2240-255-ΔN93-LEDGF and LANA1-31-ΔN93-LEDGF respectively. Numbers indicate the different amino acid residues. AT, AT-Hook; CR, Charged Region; SRD, Supercoiled Recognition Domein; IBD, Integrase Binding Domain; PWWP, Pro-Trp-Trp-Pro Domain; PFV, Prototype foamy virus; LANA, Latency associated nuclear antigen; HPV, Human papilloma virus; LEDGF, Lens epithelium-derived growth factor; NLS, Nuclear localization signal.