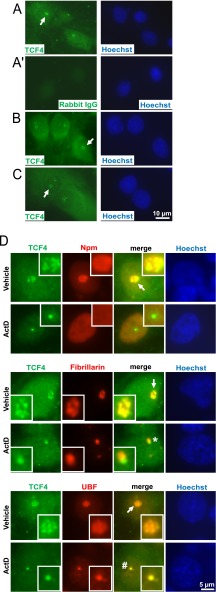
Fig. 6.
Nucleolar presence of the transcription factor TCF4 in primary cultures of forebrain neurons and astrocytes. Cultured rat brain cells were immunostained for TCF4 and the nucleolar markers as indicated. A, Representative images depicting TCF4 immunofluorescence in DIV6 cortical neurons. Both diffused and fine granular signals were observed in the nucleus and the perikaryon. In addition, nucleolus-like structures were detected (arrows). A', No signal was observed with a control IgG. Similar TCF4 staining pattern including nucleolar-like structures was found in DIV7 hippocampal neurons (B) and in DIV10 primary astrocytes (C). D, Representative nuclear profiles of DIV6 cortical neurons following 6h treatment with 0.1% DMSO (vehicle) or 1 μm ActinomycinD (ActD); magnified images of the nucleoli are shown in the insets. Note that the TCF4 signal shows the most extensive overlap with fibrillarin and only a partial overlap with Npm or UBF suggesting its localization to the transcriptionally active DFC. After transcriptional inhibition, TCF4, fibrillarin and UBF remained associated with the nucleolus. Note that fibrillarin and TCF4 segregated into distinct structures (indicated by a star) whereas UBF and TCF4 overlapped (indicated by a hash sign). Such a segregation pattern resembles fibrillar caps that sequester core components of the nucleolar transcription machinery (see text for details). The co-localization and/or separation of TCF4 and nucleolar markers was confirmed by quantitative analysis of images from panel D (supplemental Fig. S4).