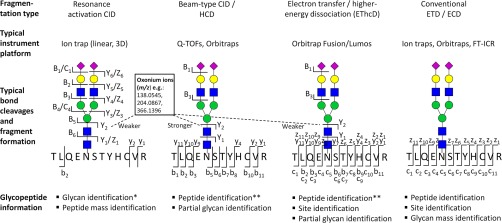
Fig. 4.
The main dissociation methods in glycoproteomics, typically used in conjunction i.e. resonance activation (ion trap type) CID, beam-type (Q-TOF type) CID or HCD, hybrid-type EThcD, and the conventional ETD (or ECD) fragmentation. The resulting bond cleavages and fragment ion formations when applied to N-glycopeptides are indicated including the presence of diagnostic oxonium ions (insert) (116, 117). *N-Glycan identification is usually restricted to specification of the monosaccharide composition and the partial or complete topology. **The b/y-ions in the beam-type CID (HCD) and EThcD dissociation schemes usually lose the conjugated glycan and therefore do not provide information about the glycosylation site.