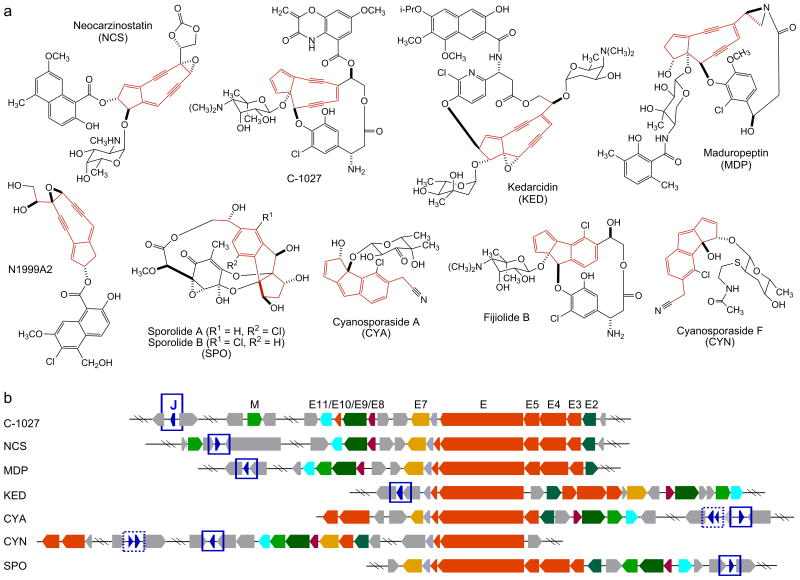
Figure 1.
Structures of the 9-membered enediyne natural products and their biosynthetic gene clusters. (a) Structures of the five 9-membered enediyne natural products (NCS, C-1027, KED, MDP, N1999A2) and the four additional natural products (fijiolide, SPO, CYA, CYN) proposed to be derived from 9-membered enediyne precursors after cycloaromatization. The 9-membered enediyne cores or their aromatized products are highlighted in red. (b) Alignment of the seven known 9-membered enediyne biosynthetic gene clusters highlighting the enediyne PKS gene cassette (i.e., E3, E4, E5, E, E10) (shown in red) and the seven additional conserved genes (i.e., E2, E7, E8, E9, E11, M, J) (color-coded). C-1027 biosynthetic gene cluster nomenclature is used. SgcJ and its homologues reported in this study are shown in blue and highlighted with blue boxes. Additional SgcJ homologues were also noted in the CYA and CYN clusters (boxed with dotted blue lines), but they were not included in the current study due to their varying length and significantly lower amino acid sequence homology.