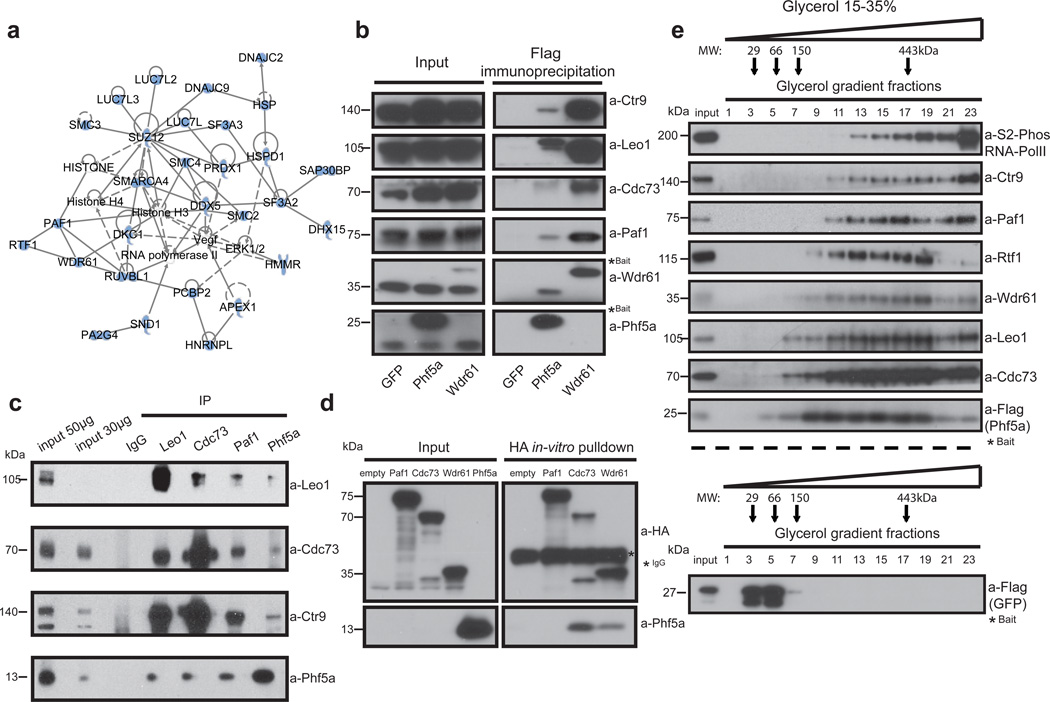
Figure 3. Phf5a physically associates with the Paf1 complex.
(a) Ingenuity systems-generated pathway of Phf5a interacting proteins following purification and mass spectrometry in ESCs. Solid or dashed lines illustrate established direct or indirect interactions, respectively. (b) Validation of Phf5a interactions with the Paf1 complex in ESCs using Flag-Phf5a purification. Tagged Phf5a, Wdr61 (positive control) and GFP (negative control) were transiently expressed in engineered Tet-inducible ESC lines following addition of doxycycline. Bait proteins are tagged (marked with a star) and migrate slower than endogenous proteins (see Supplementary Figure 7). (c) Endogenous protein immunoprecipitations for Phf5a and Paf1C subunits in ESCs (see Supplementary Figure 7). (d) Paf1-complex subunits Paf1, Cdc73 and Wdr61 were cloned in HA-tag expressing vectors and subjected into in-vitro transcription and translation. Phf5a protein was expressed and purified from bacteria. In vitro binding of HA-tagged subunits and Phf5a was interrogated by a pull-down assay using HA-immunoprecipitation and western blot analysis (see Supplementary Figure 7). (e) Phf5a interacting proteins from ESCs were subjected to glycerol gradient sedimentation followed by fractionation and western blot analysis resulting in overlapping distributions of Phf5a and Paf1-complex subunits. A control analysis for GFP is shown in the lower panel. (see Supplementary Figure 7).