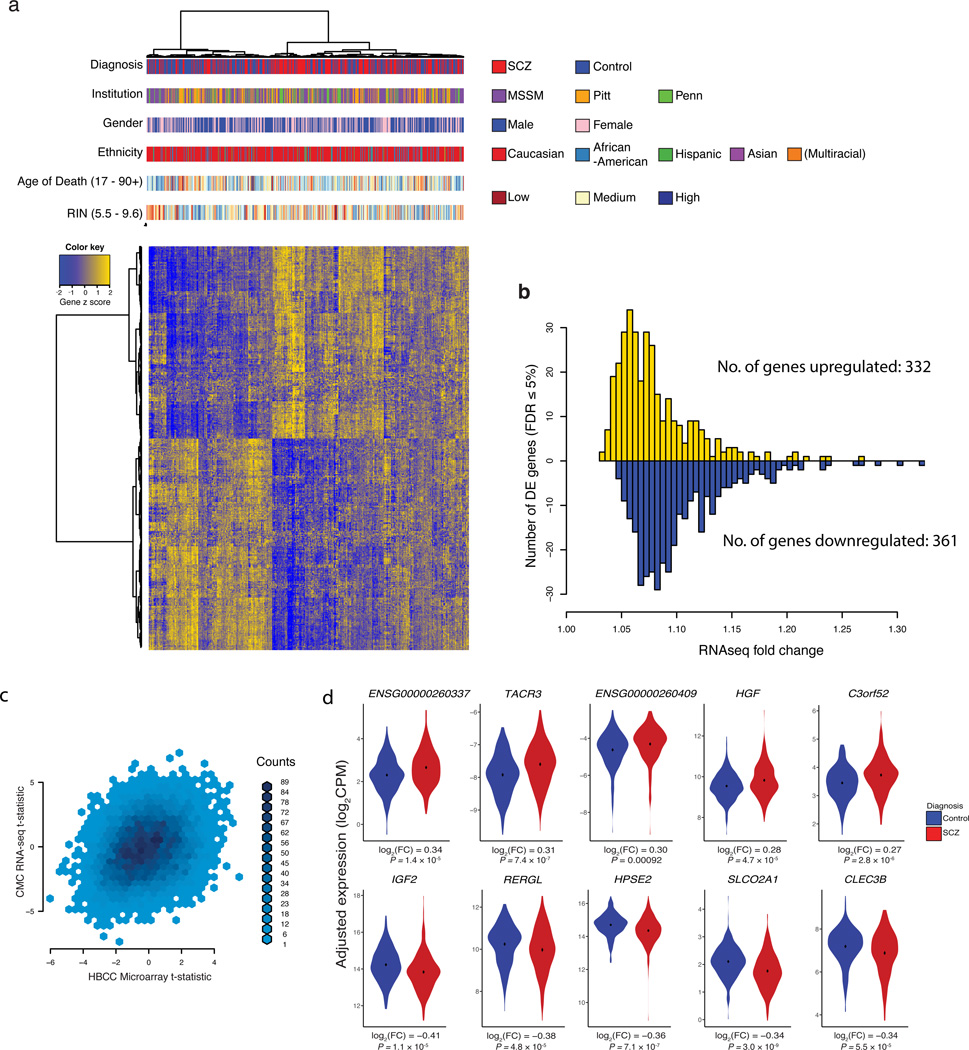
Figure 5. Differential expression between schizophrenia cases and controls in the DLPFC.
(a) For the N = 693 genes differentially expressed at FDR ≤ 5%, bivariate clustering of individuals (columns) and genes (rows) depicts the case-control differences, as marked by the red-blue horizontal colorbar at top (‘Diagnosis’). An individual’s expression (converted to a z-score per gene) is red for above-average values, and green for below-average values; thus, the top cluster of the plot consists of genes up-regulated in cases versus controls (green in top left; red in top middle), and the bottom cluster of down-regulated genes (red in bottom left; green in bottom middle). In addition to the horizontal colorbar marking case-control status for each sample, additional colorbars denote brain bank (‘Institution’), gender, reported ancestry (‘Ethnicity’), age of death, and RNA quality (‘RIN’), where the latter two use a continuous-values color scale (with low, medium, and high as colored), relative to the range denoted on the figure. (b) Distribution of fold-change of differential expression for 693 differentially expressed genes. Case:control fold-changes for up-regulated genes are plotted in red (N = 332, positive values), and control:case fold-changes for down-regulated genes in green (N = 361, negative values). (c) Binned density scatter plot comparing the t-statistics for case versus control differential expression between the independent HBCC replication cohort assayed on microarrays and the CommonMind RNA-seq data; correlation between the statistics is 0.28 (P < 10−16). (d) For the 10 significantly differentially expressed genes with the largest fold changes (5 up- and 5 down-regulated), the 25 cases and 25 controls of normalized and adjusted gene expression in cases (red) versus controls (blue).