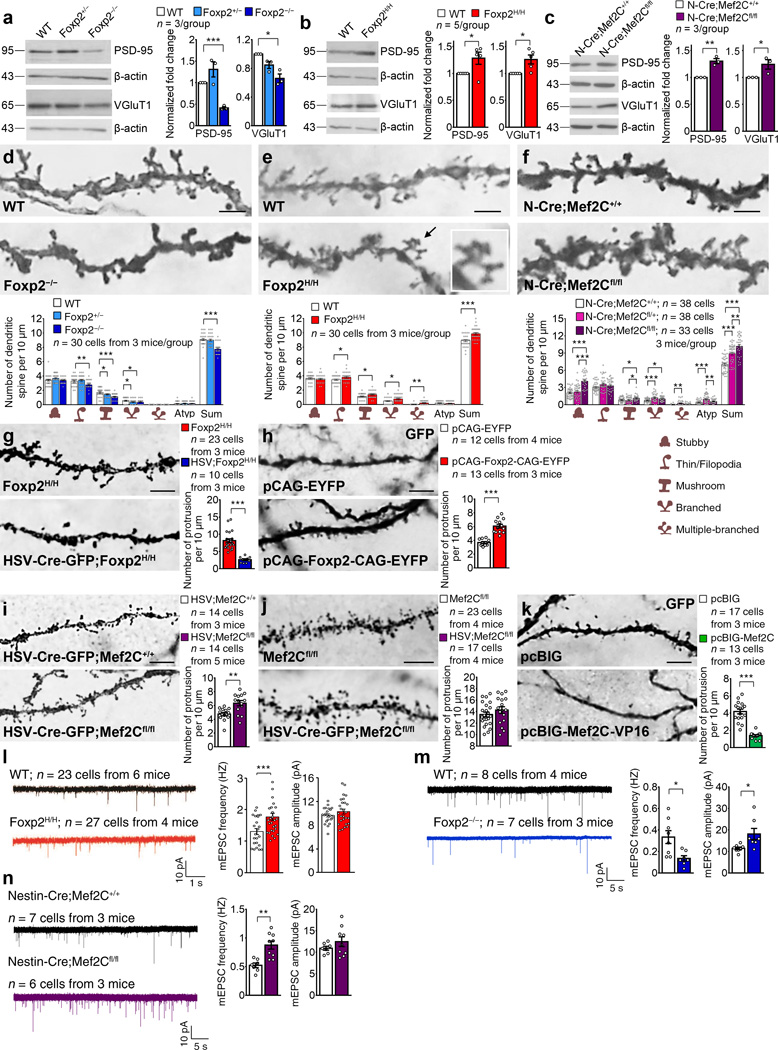
Figure 3.
Synaptic proteins and dendritic spines of SPNs are oppositely regulated by Foxp2 and Mef2C. (a–c) Western blots showing expression of PSD-95 and VGluT1 proteins in the P12 Foxp2−/− striatum (a), P14 Foxp2H/H striatum (b) and P14 Mef2C knockout striatum (c). Data represent at least three mice per genotype. Full-length blots are presented in Supplementary Fig. 10. (d–f) Golgi staining showing dendritic spines in dorsolateral SPNs of Foxp2−/− mice (d), Foxp2H/H (e) and Mef2C knockout (f) mice. Inset in e: multiple-branched spines. Data represent at least 30 cells from three mice per genotype. Atyp: atypical. Scale bars: 2.5 µm. (g) Intrastriatal injection of HSV-Cre-GFP virus in P2 Foxp2H/H mice decreases spine density in GFP-positive SPNs at P8. (h) In utero electroporation of pCAG-EYFP-CAG-Foxp2 at E13.5 increases spines of P14 wildtype SPNs. Scale bar: 5 µm. (i,j) Intrastriatal injection of HSV-Cre-GFP virus in Mef2Cfl/fl mice at P2 increases spines in GFP-positive SPNs at P8 (i), but the same injection at P14-P15 does not affect spine counts at P19-P20 (j). Scale bars: 5 µm. (k) In utero electroporation of pcBIG-Mef2C–VP16 at E12.5 decreases spines of P14 wildtype SPNs. Scale bar: 5 µm. Data in g–k represent at least 10 cells from three mice per group. (l–n) mEPSC recordings of SPNs in Foxp2H/H (l), Foxp2−/− (m), and Mef2C knockout (n) mice. Data represent at least 7 cells from at least three mice per genotype. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Error bars represent s.e.m. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD post hoc test are used in a, for VGluT1, F(2, 6) = 14.649, P = 0.005; for PSD-95, F(2, 6) = 19.954, P = 0.002, d”, for stubby, F(2, 87) = 2.992, P = 0.055; for thin/filopodia, F(2, 87) = 8.396, P = 0.000463; for mushroom, F(2, 87) = 12.889, P = 0.000013; for branched, F(2, 87) = 4.169, P = 0.019; for atypical, F(2, 87) = 0.293, P = 0.747; for sum, F(2, 87) = 28.470, P = 0.000000, f”, for stubby, F(2,106) = 34.658, P = 0.000000; for thin/filopodia, F(2,106) = 2.012, P = 0.139; for mushroom, F(2,106) = 5.182, P = 0.007; for branched, F(2,106) = 9.555, P = 0.000153; for multiple branched, F(2,106) = 5.965, P = 0.004 for atypical, F(2,106) = 11.944, P = 0.000021; for sum, F(2,106) = 38.448, P = 0.000000. Student’s t test are used in b, for VGluT1, t(8) = −3.155, P = 0.014; for PSD-95, t(8) = 2.518, P = 0.036, c, for PSD-95, t(4) = −6.442, P = 0.003; for VGluT1, t(4) = −2.795, P = 0.049, e”, for stubby, t(29) = 0.623, P = 0.538; for thin/filopodia, t(29) = −2.249, P = 0.032; for mushroom, t(29) = −2.041, P = 0.050; for branched, t(29) = −2.300, P = 0.029; for multiple branched, t(29) = −3.525, P = 0.001, for atypical, t(29) = 0.769, P = 0.448; for sum, t(29) = −4.216, P = 0.000383, g, t(31) = 9.429, P = 0.000000, h, t(23) = −7.612, P = 0.000001, i, t(26) = −3.509, P = 0.002, j, t(38) = −1.122, P = 0.269, k, t(28) = 9.453, P = 0.000000, l, for frequency, t(13) = 2.890, P = 0.013; for amplitude, t(13) = −2.2505, P = 0.043, and n, for frequency, t(14) = −4.022, P = 0.001, for amplitude, t(14) = −1.131, P = 0.237. Mann-Whitney U test are used in m, U = 167.5, P = 0.009 for frequency and U = 273, P = 0.471 for amplitude.