FIGURE 5.
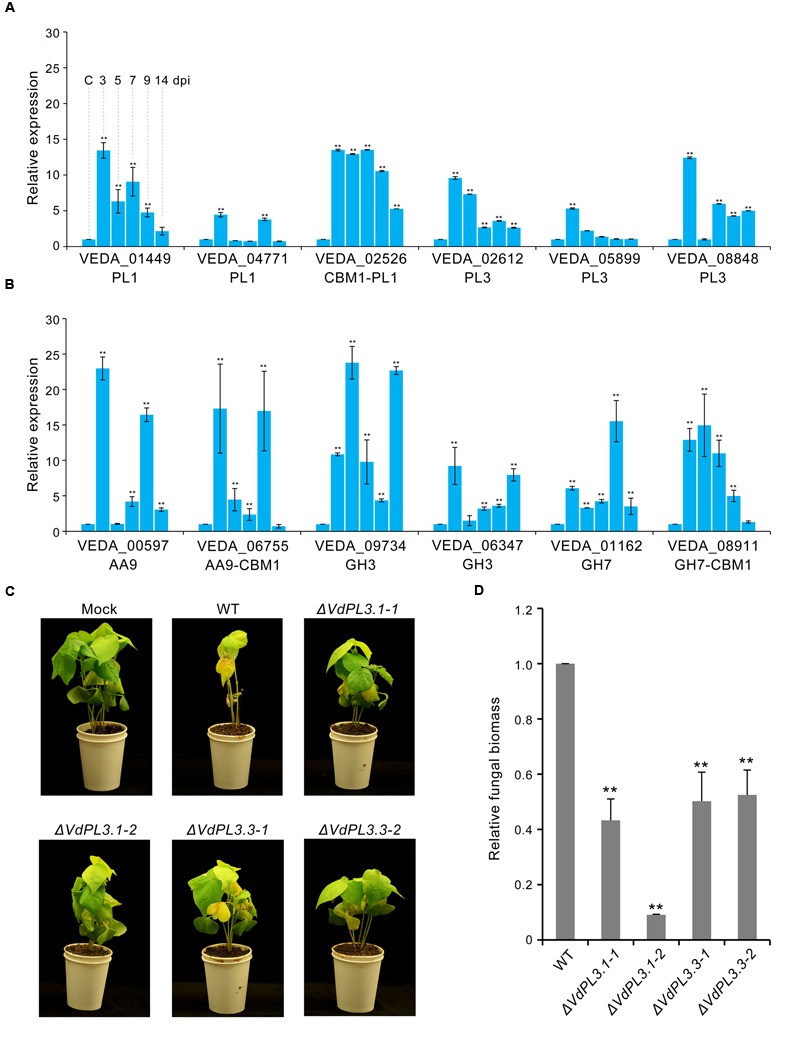
Virulence function analysis of identified proteins in the exoproteome. (A) Expression of genes involved in pectin degradation in V. dahliae infection on cotton roots determined via qRT-PCR. The control (capital letter C) shows the expression level of genes in a mixture of non-inoculated conidial and cotton root tissue; the housekeeping gene β-tubulin (VDAG_10074) was used as an endogenous control. Error bars show standard error, ∗∗ denotes statistical significance (P ≤ 0.01) of different time points compared to control using an unpaired Student’s t-test. (B) Expression of genes involved in cellulose degradation by V. dahliae. (C) Phenotypes of cotton seedlings inoculated with VdPL3.1 and VdPL3.3 gene-deletion strains. Two-week-old seedlings of susceptible cotton, Gossypium hirsutum L., ‘Junmian No.1,’ were inoculated with sterile water (Mock), wild-type (WT) V. dahliae, and the two independent VdPL3.1 and VdPL3.3 gene-deletion strains. (D) Fungal biomass of the gene-deletion strain on cotton was determined using qRT-PCR. Error bars represent standard error, and ∗∗ denotes statistical significance (P ≤ 0.05) of gene-deletion strains compared to WT using an unpaired Student’s t-test.
