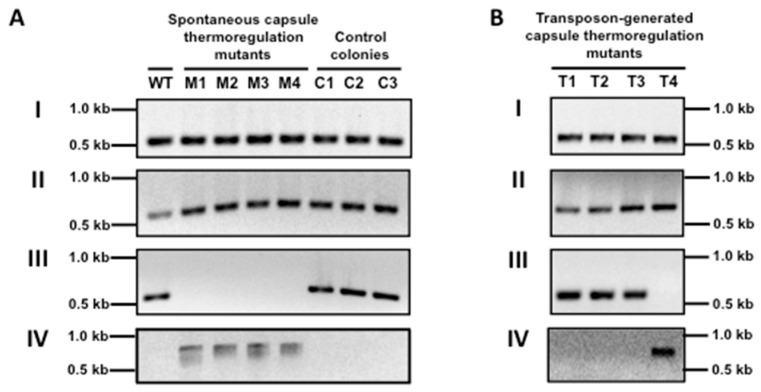
Figure 3.
PCR assay to determine the presence of prophages on the chromosome of Streptococcus pyogenes strains. (A) Deletion of ΦHSC5.3 in spontaneous capsule thermoregulation mutants. Spontaneously generated capsule thermoregulation mutants producing a large amount of the capsule regardless of incubation temperature were screened after passaging the background strain CovRIFD in THY medium. Control colonies still displaying capsule thermoregulation on the same plates were also selected for this assay. PCR was performed to determine the presence of prophages using the primers to amplify a portion of a gene in ΦHSC5.1 (I), ΦHSC5.2 (II), or ΦHSC5.3 (III), or primers that amplify HSC5 chromosomal DNA only when ΦHSC5.3 was cured (IV). Strains used: WT (wild-type), HSC5; M1–M4 (mutant strains), randomly chosen four spontaneously arisen capsule thermoregulation-negative mutants; C1–C3 (control strains), colonies still showing capsule thermoregulation after passaging; (B) The existence of ΦHSC5.3 in the transposon-generated mutants. Since the excision of ΦHSC5.3 occurs spontaneously and influences capsule thermoregulation, the presence of ΦHSC5.3 in the previous transposon-generated mutants was determined through PCR. The same primers were used as those used in Figure. A. Strains used: T1–T4 (transposon-generated capsule thermoregulation mutants), a transposon insertion occurred in the gene L897_07695 in ΦHSC5.3 (T1), at or near the ribosome binding site of cvfA (T2 and T3, previously described as CovRIFD:TnCvfA1 and CovRIFD:TnCvfA2, respectively [10]), or in the intergenic region (IGR) immediately upstream of the capsule operon (T4).