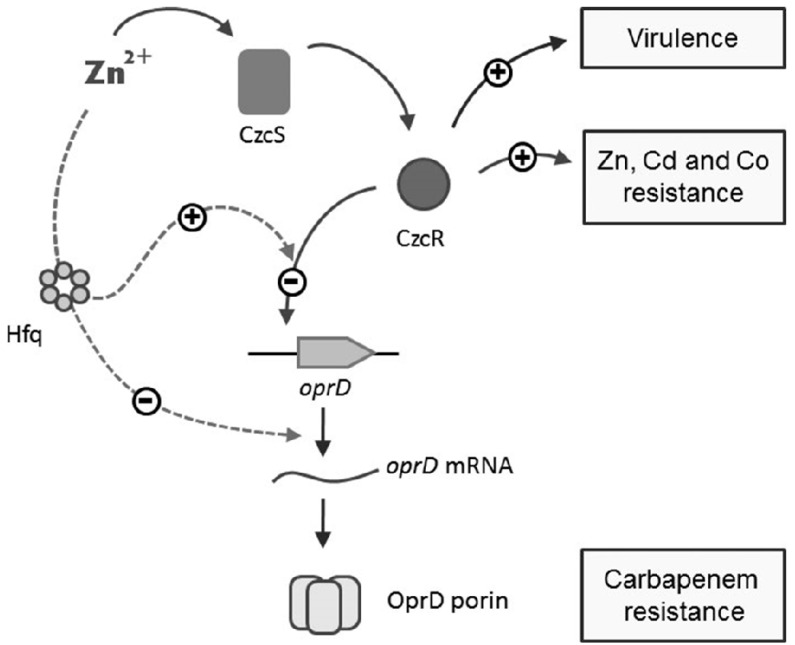
Figure 6.
Co-regulation mechanism linking metal resistance, virulence and carbapenem resistance. Zn activates the CzcS sensor protein that will in turn activates the CzcR transcriptional regulator. CzcR induces the expression of CzcCBA efflux pump involved in Zn, Cd and Co resistance [7] and act positively on the virulence of P. aeruginosa [9]. CzcR is also implicated in the repression oprD transcription yielding to carbapenem resistance [7]. The RNA chaperone Hfq is necessary for the binding of CzcR to the oprD promoter leading to transcriptional repression. Additionally a Zn-inducible, Hfq-dependent mechanism decreases the amount of oprD mRNA yielding to an alternative pathway inducing carbapenem resistance in presence of Zn, and even in the absence of CzcR. Overexpression of the CopR protein, either by Cu or artificially, represses OprD only in the presence of the RNA chaperone Hfq. Additionally CopR is able to induce the expression of CzcR [5].