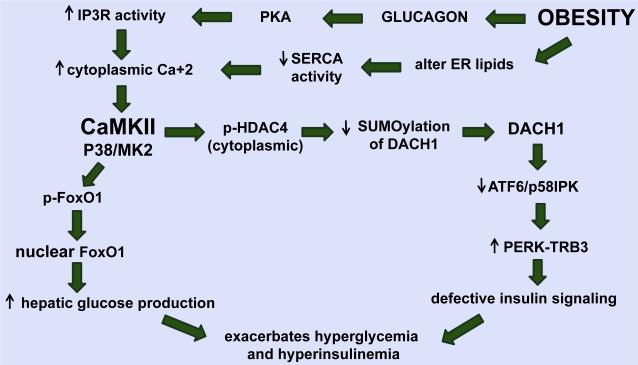
Fig. 2.
Illustration showing how the CaMKII–MK2 pathway may exacerbate hyperglycaemia and hyperinsulinaemia in obesity. Obesity-induced activation of CaMKII increases hepatic glucose production through regulating the nuclear localization of FoxO1. Activated CaMKII also alters hepatic insulin signalling through HDAC4–DACH1-mediated activation of the ATF4–TRB3 pathway which further exacerbates hyperglycaemia and hyperinsulinaemia. PKA, protein kinase A; IP3R, inositol triphosphate receptor; SERCA, sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum calcium-adenosine triphosphatase; CaMKII, calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II; p38, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; MK2, mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2; FoxO1, forkhead box protein O1; p-HDAC4, phosphorylated-histone deacetylase 4; DACH1, dachshund homolog 1; ATF6, activating transcription factor 6; p58IPK, double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase inhibitor; protein kinase RNA-like ER kinase; Trb3, Tribbles homolog 3.