Figure 7.
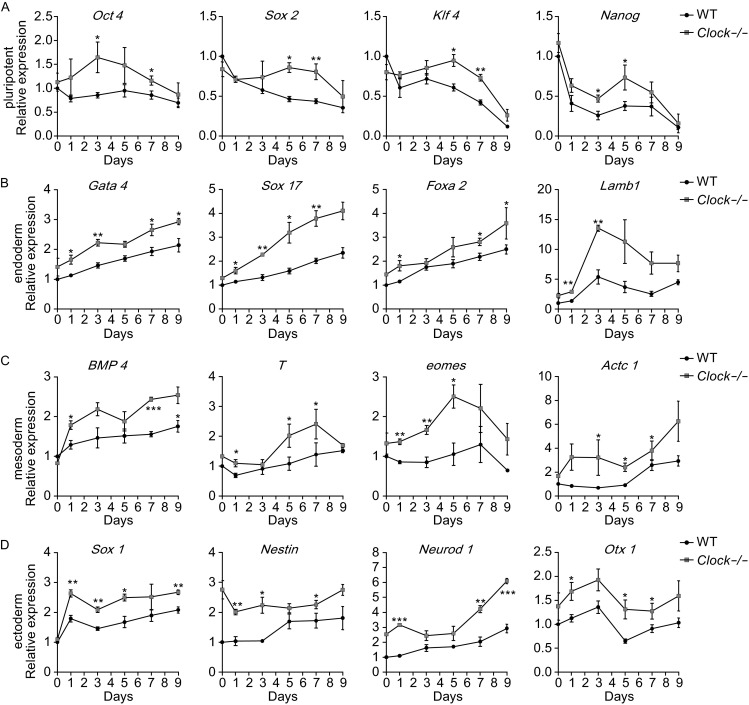
Clock silencing promoted the expression of genes controlling the three embryonic germ layers in spontaneously differentiated mESCs. (A) Relative mRNA expression of pluripotent markers Oct4, Sox2, Nanog, and Klf4 after spontaneous differentiation in wild type and Clock-/- mESCs. Expression of the pluripotent genes was gradually decreased in wild type and Clock-/- mESCs. (B) Relative mRNA expression of endoderm markers Gata4, Sox17, Foxa2, and Lamb1 after spontaneous differentiation in wild type and Clock-/- mESCs. Clock-/- mESCs exhibited a higher expression of these endoderm genes. (C) Relative mRNA expression of mesoderm markers BMP4, T, Eomes, and Actc1 after spontaneous differentiation in wild type and Clock-/- mESCs. Clock-/- mESCs exhibited a higher expression of mesoderm genes. (D) Relative mRNA expression of ectoderm markers Nestin, Sox1, Neurod1, and Otx1 after spontaneous differentiation in wild type and Clock-/- mESCs. Clock-/- mESCs exhibited a higher expression of these ectoderm genes. The mRNA expression levels were normalized with that of the endogenous GAPDH. Data represent the average of three independent experiments and are presented as means ± S.D. Statistical significance was calculated using the Student’s t-test: *denotes P < 0.05, **denotes P < 0.01, ***denotes P < 0.001 compared with the Ctrl group, ns, not significant
