Figure 1.
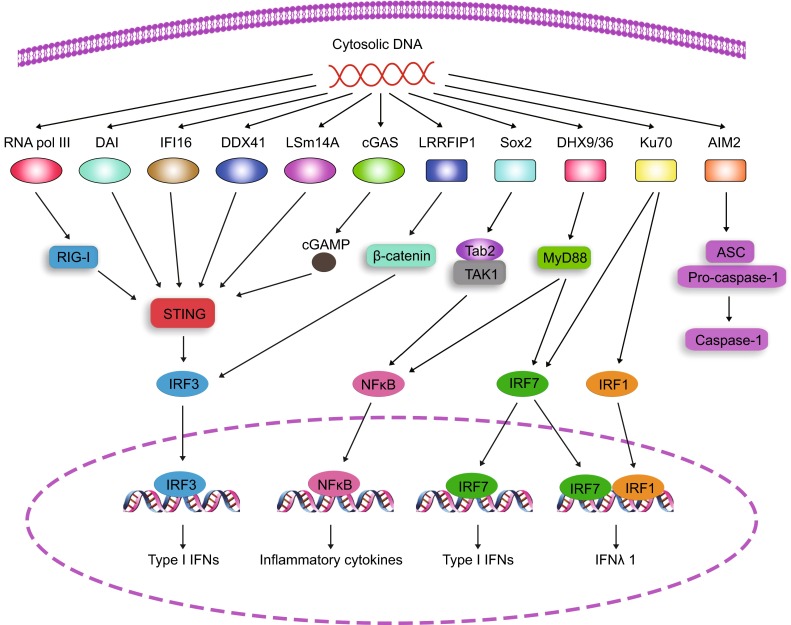
Signaling pathways of cytosolic DNA sensors with DNA challenge. Up to now, many cytosolic DNA sensors have been defined to detect intracellular double-stranded DNAs. RNA polymerase III transcribes AT-rich DNAs into RNAs that are recognized by RNA sensor RIG-I, followed by STING and IRF3 activation. DNA sensors DAI, IFI16, DDX41 and LSm14A sense dsDNA directly to activate STING for type I IFN production. In the presence of dsDNAs, cGAS catalyzes the synthesis of cGAMP, a strong activator of STING. With dsDNAs, LRRFIP1 initiates β-catenin and IRF3 activation in a STING-dependent manner. Other DNA sensors prime immune responses independently of STING. After recognition of dsDNAs, Sox2 triggers the activation of the Tab2/TAK1 complex in neutrophils. When detected by dsDNAs, DHX9/36 activates NFκB and IRF7 through MyD88. DNA sensor Ku70 triggers the activation of IRF1 and IRF7. AIM2 initiates the activation of inflammasome through ASC with DNA binding
