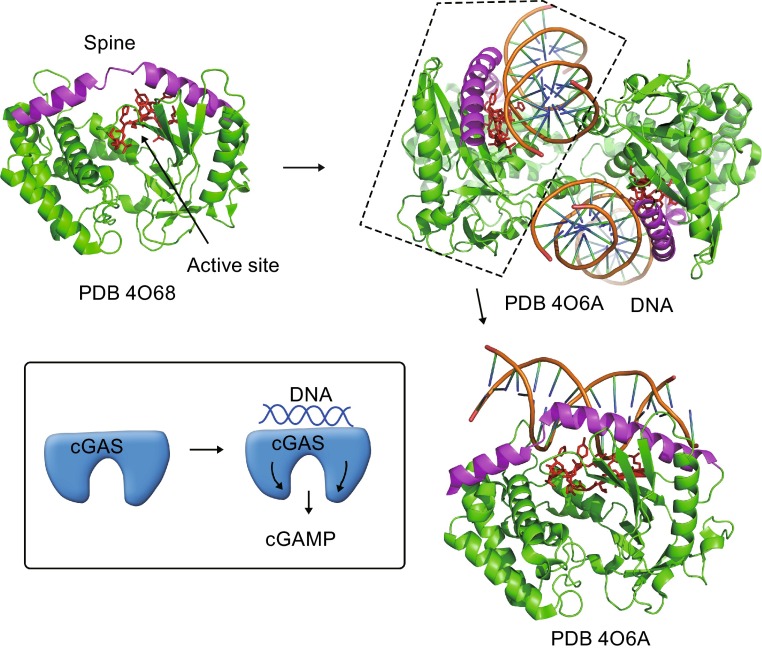
Figure 2.
Structural basis of cGAS binding to DNA. In a resting state, cGAS exists with a monomer form. The DNA binding site comprises helices that form a flat spine. Post DNA binding, cGAS forms dimerization and undergoes conformational changes that render the spine region twisted, promoting synthesis of cGAMP. Inset is an illustration of cGAS activation upon binding DNA