FIGURE 4.
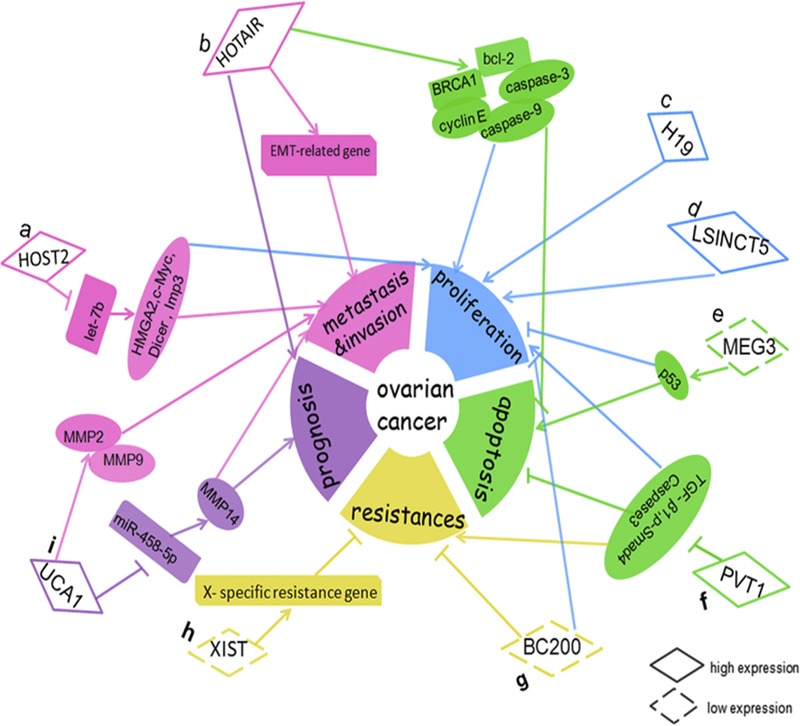
Dysregulation and functional roles of lncRNAs in OC. A, HOST2 could increase cell metastasis, invasion, and proliferation via binding to let-7b and inhibiting the function of let-7b, and then increase expression of its target genes (HMGA2, c-myc, Dicer, and Imp3). B, HOTAIR represented a prognostic marker and increased cell metastasis and invasion by regulating EMT-related genes; HOTAIR promoted SOC cell proliferation and decreased cell apoptosis by regulating certain cell cycle– and apoptotic-related genes (cyclin E, BCL-2, caspase-9, caspase-3, and BRCA1). C, H19 increased cell proliferation. D, LSINCT5 increased cell proliferation. E, MEG3 promoted cell proliferation and decreased cell apoptosis via p53. F, PVT1 inhibited cell apoptosis and increased cell proliferation and carboplatin resistance in OC by knockdown the expression of TGF-β1, p-smad4, and Caspase-3. G, BC200 inhibited OC cell proliferation and increased the sensitivity of OC cells to carboplatin. H, XIST could inhibit OC cell resistance to paclitaxel via reactivating the X-specific resistance gene. I, UCA1 promoted invasion and metastasis by up-regulating MMP2 and MMP9 expression in OC cells; UCA1 represented a prognostic marker and enhanced EOC metastasis through the UCA1-miR-485-5p-MMP14 axis.
