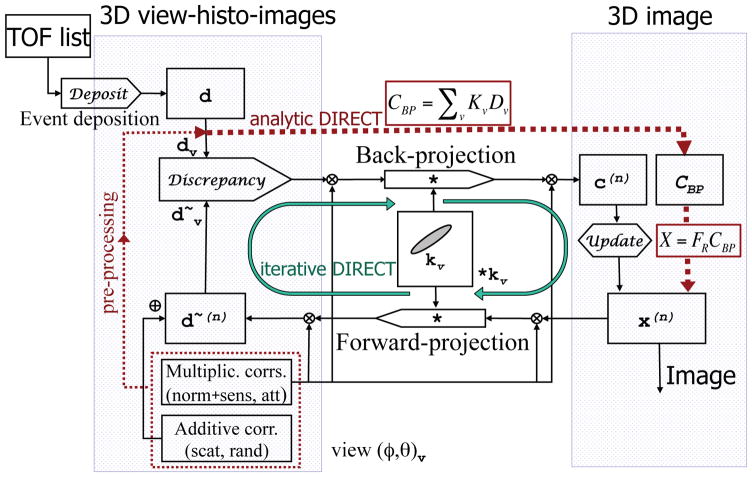
Figure 5.
Flowchart summarizing DIRECT corrections, reconstruction paths and data structures. Both iterative (green solid line loop) and analytic algorithms (red dotted line) use the same data/correction structures (histo-images) and basic reconstruction tools (DIRECT forward/back-projectors). Each 3D view-grouped histo-image contains all events from a given “view” (ϕ, θ)v (comprising a range of azimuthal and co-polar angles). All data and corrections are in the same histo-image format. Forward- and back-projections are 3D convolution-like operations involving the proper 3D TOF resolution kernel kv (taking into account TOF, detector, and image resolution functions) for each view v. Discrepancy and Update operators are specifically defined by each particular algorithm; for example, and x(n + 1) = c(x) x(x), respectively, for ML-EM algorithm, where dv are measured data, are forward-projected data estimates (including corrections) from image x(n) at iteration n, and c(n) is the correction image at iteration n derived from the back-projection of the discrepancy operator. Back-projection (CBP) and reconstruction filter (FRCBP) operations for analytic-DIRECT are shown in spectral forms (see details in 3.1).