Figure 4.
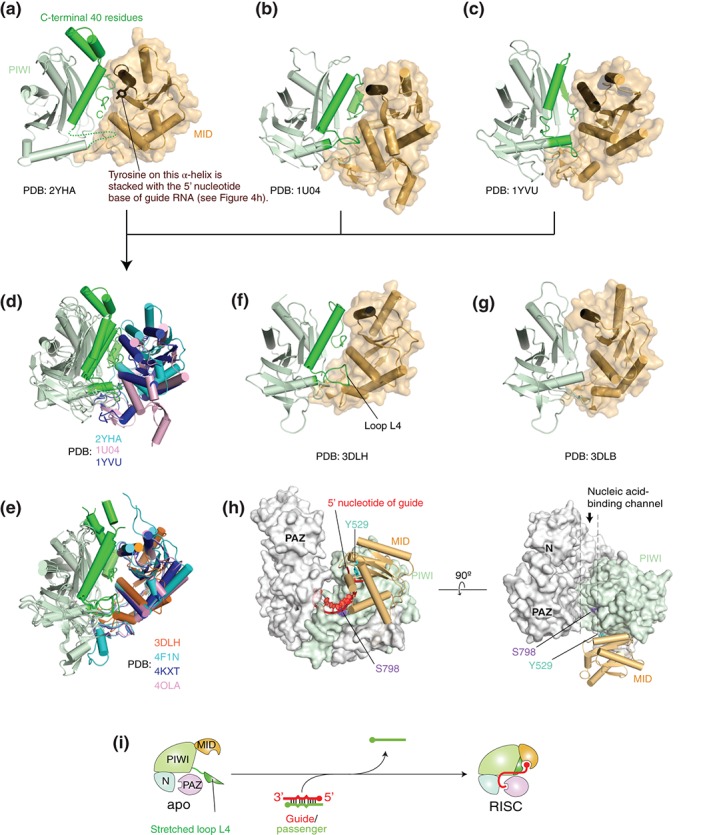
Structural evidence of an open conformation of guide‐free AGO proteins. (a–c) Crystal structures of Neurospora crassa QDE2 MID–PIWI domains (a: PDB ID: 2YHA), Pyrococcus furiosus AGO (b: PDB ID: 1U04), and Aquifex aeolicus AGO (c: PDB ID: 1YVU). For clarity, only the MID (wheat) and PIWI (light green) domains are shown in the ribbon models. The corresponding C‐terminal region that is disordered in TtAGO in complex with a guide of 10 nucleotide (nt) (see g) is colored in green. The MID domain is also drawn as a surface mode. The α‐helix on which the conserved tyrosine is stacked with the first nucleotide base of guide strand is colored in chocolate. (d) Superposed structures of (a)–(c) on their PIWI domain. The MID domains of NcQDE2, PfAGO, and AaAGO are colored in cyan, pink, and blue, respectively. Otherwise, the color code is the same as (a)–(c). (e) Superposed structures of TtAGO‐, KpAGO‐, hAGO1‐, and hAGO2‐RISCs (PDB IDs: 3DLH, 4F1N, 4KXT, and 4OLA, respectively) on their PIWI domain. The MID domains of TtAGO, KpAGO, hAGO1, and hAGO2 are colored in orange, cyan, blue, and pink, respectively. (f–g) Crystal structures of TtAGO in complex with a guide of 21 nt (f: PDB ID: 3DLH) and of 10 nt (g: PDB ID: 3DLB). The color code is the same to (a)–(c). (h) Positions of the phosphorylation sites, Y529 (cyan) and S798 (purple), on hAGO2. The structure of hAGO2‐RISC (PDB ID: 4OLA) is drawn as a surface model except for the MID domain that is shown as a cylinder model. The MID and PIWI domains are colored in wheat and light green, respectively. The bound guide RNA (red) is shown as a ribbon model. The guide is not shown on the right panel for clarity. (i) A hypothetical model of RISC assembly. Guide‐free AGO protein opens the hinged MID‐PIWI domains while the unstructured C‐terminal fragment (green) may be extended to solvent.
