Figure 5.
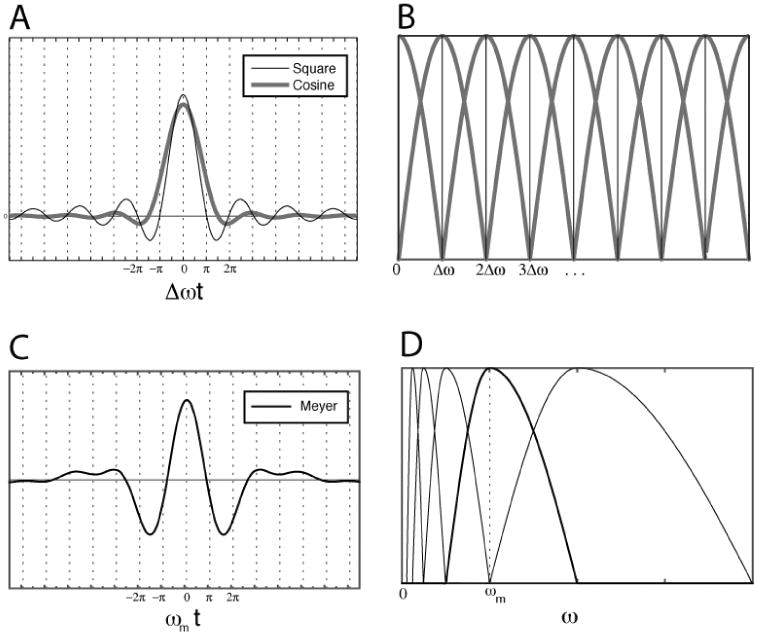
A: Time-domain envelopes corresponding to the cosine frequency window (bold line) and the square window (thin line). B: An example of frequency-domain windowing with fixed bandwidths for cosine (bold line) and square (thin line) windows. C: A Meyer wavelet function obtained by (D) joining two cosine window halves (thick line) with the same center frequency, ωm, but scaled to different bandwidths, equal, respectively, to one-half and one times ωm.
