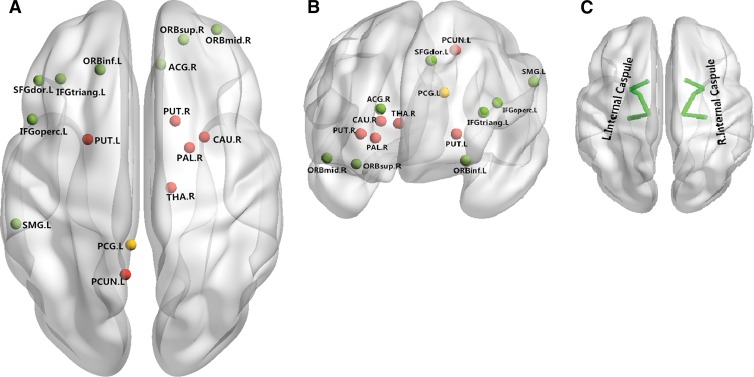
Figure 4:
Neural networks involved in ADHD mainly include the superior frontal cortex, inferior frontal cortex, and basal ganglia. Both anatomic and functional changes are shown in the, A, superior view and, B, anterior view. Red and yellow spots represent changes in gray matter volume and function, respectively; green spots indicate regions with both functional and anatomic changes. C, Main white matter bundles (green line), with changes of integrities revealed by DT imaging. ACG.R = right anterior cingulate gyrus; CAU.R = right caudate nucleus; IFGoperc.L = left inferior frontal gyrus, opercular part; IFG triang.L = left inferior frontal gyrus, triangular part; ORB inf.L = orbital part of left inferior frontal gyrus; ORBmid.R = orbital part of right middle frontal gyrus; ORB.sup.R = orbital part of right superior frontal gyrus; PAL.R = right lenticular nucleus, pallidum; PCG.L = left posterior cingulate gyrus; PCUN.L = left precuneus; PUT.L = left lenticular nucleus, putamen; PUT.R = right lenticular nucleus, putamen; SFGdor.L = left superior frontal gyrus; SMG.L = left supramarginal gyrus; THA.R = right thalamus.