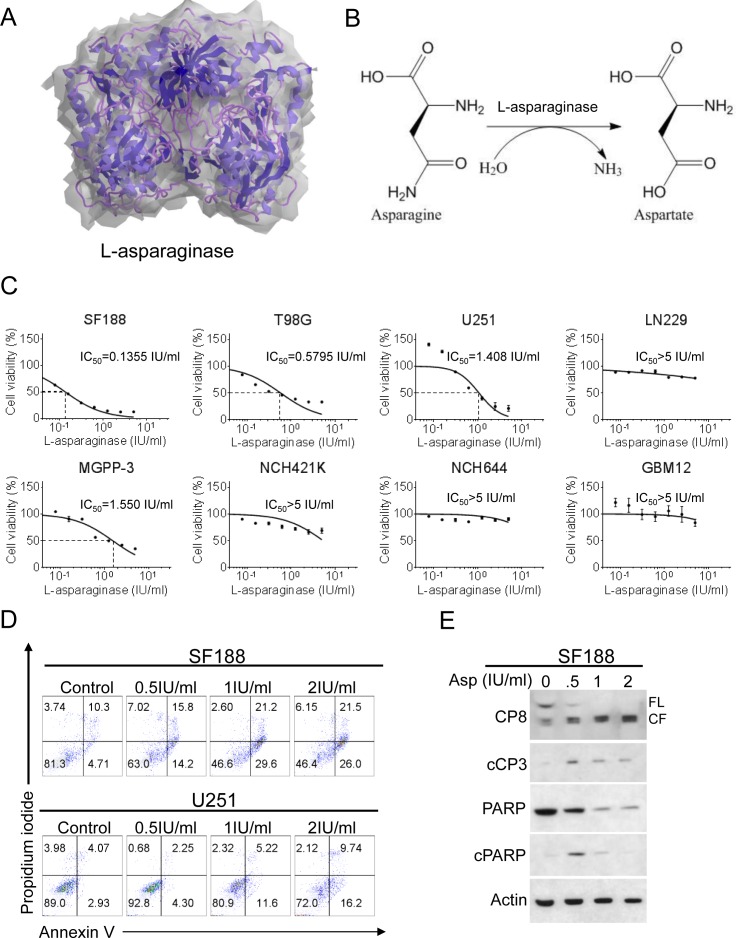
Figure 1. Treatment with L-asparaginase (Asp) inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis across different glioblastoma cells.
A., 3-dimensional graphical representation of Escherichia coli L-asparaginase. Modified with ChemBioDraw Ultra 13.0 based on PDB ID 3ECA [57], http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=3eca, last accessed 02/03/2016. B., Representation of the chemical reaction catalyzed by L-asparaginase (ChemBioDraw Ultra 13.0). C., SF188 (pediatric), T98G (adult), U251 (adult), LN229 (adult), MGPP-3 (murine, transgenically-derived) glioblastoma cells and NCH421K, NCH644 glioma stem-like cells as well as GBM12 (PDX-derived) glioblastoma cells were treated with increasing concentrations of L-asparaginase under serum starvation (1.5% FBS). After 72h, MTT assays were performed. Dose-response curves and IC50-values were calculated using non-linear regression. Data are presented as mean and SEM. D., Representative flow plots of SF188 and U251 glioblastoma cells subjected to 48h treatment with indicated concentrations of L-asparaginase prior to performing staining for annexin V and propidium iodide. E., SF188 glioblastoma cells were treated for 24h with increasing concentrations of L-asparaginase (Asp) under serum starvation (1.5% FBS). Whole-cell extracts were examined by Western blot for caspase 8 (CP8 - FL = full length form, CF = cleaved fragment), cleaved caspase 3 (cCP3), PARP and cleaved PARP (cPARP). Actin Western blot analysis was performed to confirm equal protein loading.