Figure 4. GR binds to Rad51 and disrupt Rad51-BRCA1 interaction.
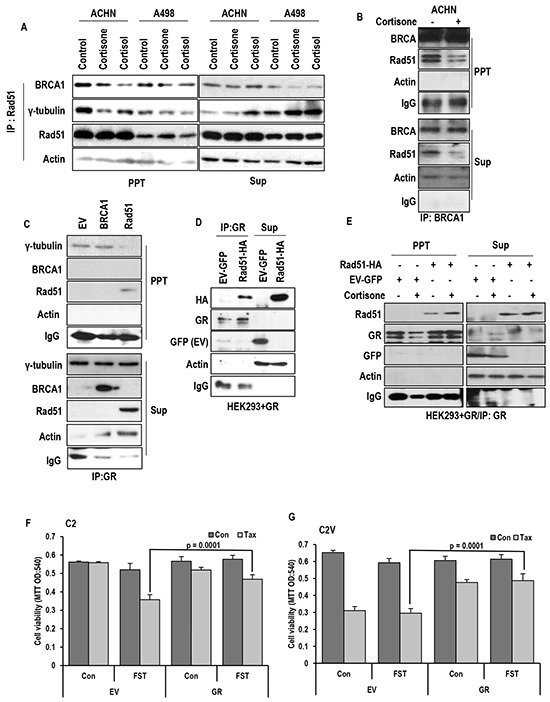
A. Cortisone (5 μM) and cortisol (5 μM) disrupt binding Rad51-BRCA1 interaction in VHL-positive ACHN cells, but tiny effect on VHL-negative A498 cells. For binding assay, immunoprecipitation (IP) analysis was performed by anti-Rad51 antibody. B. Rad51-BRCA1 binding is reduced by cortisone treatment in VHL-intact ACHN cells. Anti-BRCA1 antibody was used for IP analysis. C. GR only binds to Rad51 but not BRCA1. D. The binding of GR-Rad51 is confirmed by exogenous proteins. GFP-tagged GR and HA-tagged Rad51 were overexpressed in HEK293 cells, and lysates from these cells were used for IP analysis. E. Enhanced binding of Rad51-GR is detected by cortisone (5 μM) treatment. IP analysis was performed by anti-GR antibody. F. Taxol sensitivity induced by FST in VHL-negative C2 cells is blocked through GR overexpression. G. Cortisone induced Taxol resistance is not affected by inhibition of ER-α in VHL-intact C2V cells, which has Taxol sensitivity. After transfection for GR overexpression, Taxol (Tax; 3 μM) and Fulvestant (FST; 3 μM) were treated as indicated. 72 hr later, MTT assay was performed for measuring cell viability.
