Figure 2. Gremlin forms disulfide-bound homodimers through Cys141.
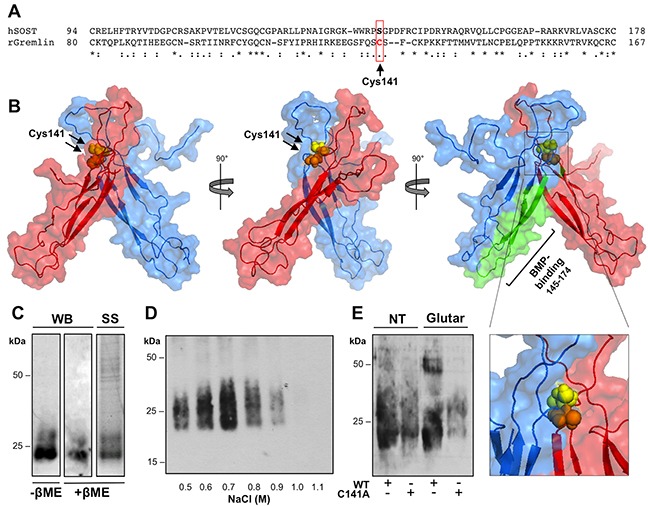
A. CLUSTAL W sequence alignment of the cystine-knot domain of gremlin and of structurally related SOST. B. surface view of the predicted structure of gremlin homodimer generated by docking simulation with RosettaDock software (model 0267; total score: −29.594; interface score −4.429; interchain contact −20). Gremlin homodimer subunits are in red or light blue. Cys141 residues are in yellow and orange spheres. The previously identified BMP4-binding region of gremlin is depicted in green. C. gremlinC141A mutant was transiently expressed in HEK293T cells and sequentially purified from cell supernatant by IMAC and heparin-affinity chromatography. Heparin column was eluted with a discontinuous NaCl gradient. Eluted fractions were separated by SDS-PAGE under non-reducing conditions and probed with anti-gremlin antibody. D. purified gremlinC141A monomer was analysed by WB under non-reducing and reducing conditions and by SS of the gel. E. Gremlin wt and gremlinC141A were incubated in the absence or in the presence of 0.05% glutaraldehyde for 20 minutes at RT, separated by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions and probed with anti-gremlin antibody.
