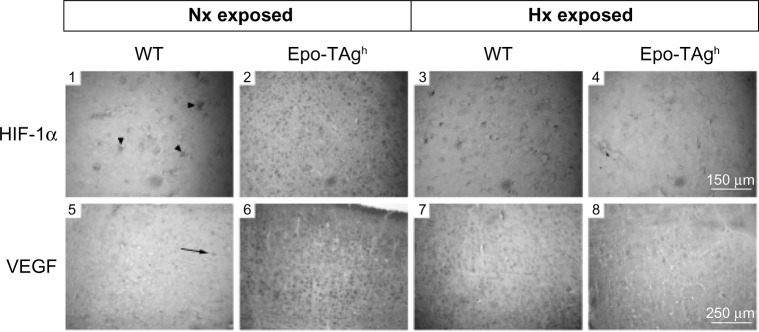
Figure 3.
Cerebral angiogenesis in Epo-TAgh mice.
Notes: Immunohistological detection of HIF-1α and VEGF at the sensory cortex level in normoxia (Nx exposed) and after chronic hypoxia exposure (Hx exposed) in WT (1, 3, 5, 7) and Epo-TAgh mice (2, 4, 6, 8). Arrowheads and arrow indicate HIF-1α (1)- and VEGF (5)-positive cells, respectively. In normoxia, Epo-TAgh mice showed an increase in HIF-1α (2)- and VEGF (6)-positive cells suggesting an enhancement of cerebral angiogenesis through the HIF-1α/VEGF pathway. In WT mice, chronic hypoxia led to an increase in HIF-1α (3) and VEGF (7), while they led a decrease in Epo-TAgh mice (4, 8). Adapted from Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. Volume 296(3). El Hasnaoui-Saadani R, Pichon A, Marchant D, et al. Cerebral adaptations to chronic anemia in a model of erythropoietin-deficient mice exposed to hypoxia. Pages: R801–R811. Copyright 2009.83
Abbreviations: Epo, erythropoietin; Epo-TAgh mice, Epo-deficient mice; HIF-1α, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; Hx, hypoxia; Nx, normoxia; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; WT, wild type.