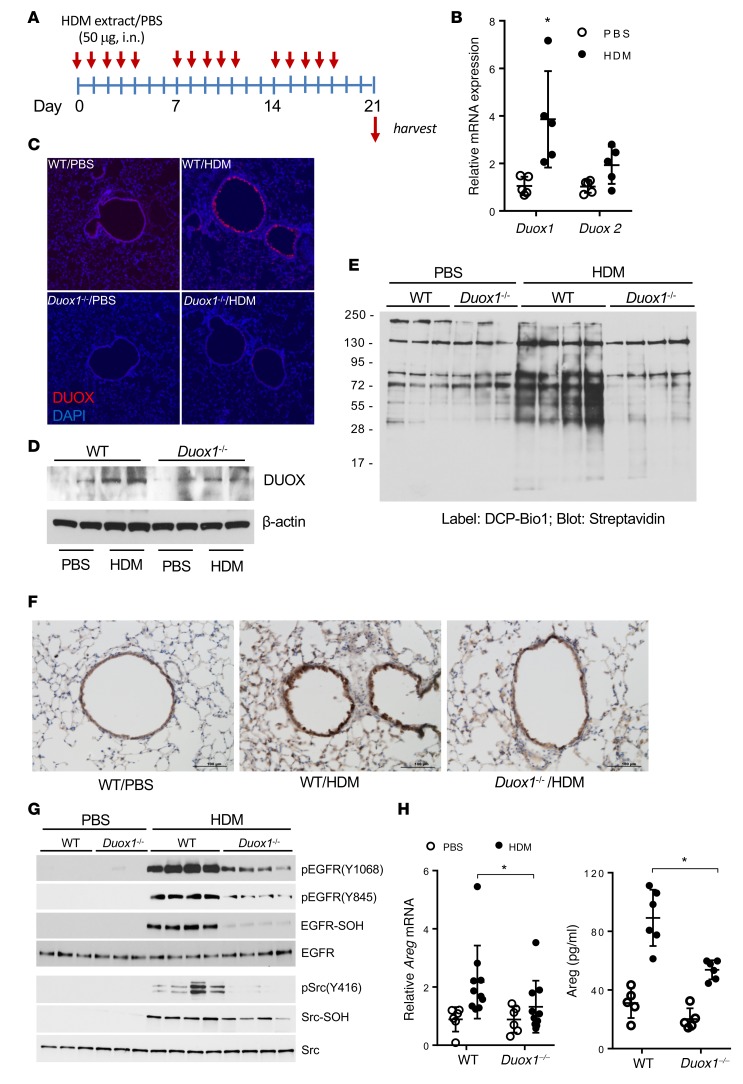
Figure 2. DUOX1 contributes to oxidative EGFR activation in house dust mite–induced allergic asthma in mice.
(A) Experimental design of house dust mite–induced (HDM-induced) allergic inflammation. (B) Analysis of DUOX1 and DUOX2 mRNA in lung tissues. (C and D) Analysis of DUOX1 protein expression in lung tissues using immunofluorescence (C; nuclei counterstained in blue; original magnification ×10) or Western blot analysis (D). (E) Analysis of protein cysteine sulfenylation by DCP-Bio1 labeling of lung tissue homogenates and streptavidin blotting. (F and G) Analysis of EGFR activation by IHC for phosphorylated EGFR (Y1068) (F) and Western blot analysis of lung tissue homogenates for tyrosine phosphorylation and cysteine oxidation (-S-OH, using DCP-Bio1 labeling) within EGFR or Src (G). Scale bars: 100 μm. (H) Quantitation of lung tissue Areg mRNA expression and Areg levels in BAL fluids. Qualitative data are representative of 3 separate experiments. Dot plots indicate mean ± SD of 6–10 replicates from 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.05 compared with corresponding controls, by 2-way ANOVA.