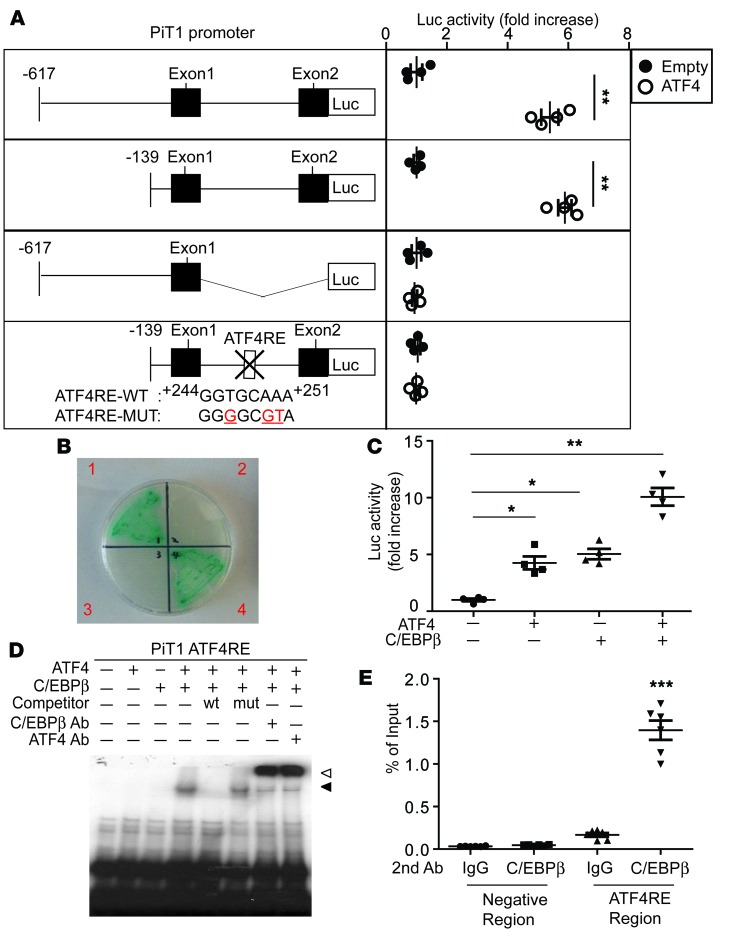
Figure 6. The transcriptional regulation of PiT1 by the ATF4-C/EBPβ complex.
(A) Deletion and mutational analysis of the PiT1 gene using a luciferase (Luc) reporter gene assay. The schematic illustrations represent the serially deleted PiT/Luc reporter constructs. Results are expressed as the relative Luc/β-galactosidase units of induction (n-fold) over the control value for each construct. (B) Yeast 2-hybrid screen. Y2HGold yeasts expressing ATF4 and/or C/EBPβ were grown onto an SD agar plate placing 4 amino acids (Leu, Trp, Ade, and His) in the presence of X-α-Gal and Aureobasidin A. Quadrant 1 of the plate contained a bait vector, pGBKT7-Atf4, and a prey vector, pGADT7-C/ebpβ; quadrant 2 contained a bait vector, pGBKT7-Atf4, and a prey vector, pGADT7-Empty; quadrant 3 contained a bait vector, pGBKT7-C/ebpβ, and a prey vector, pGADT7-Empty; and quadrant 4 contained a bait vector, pGBKT7-C/ebpβ, and a prey vector, pGADT7-Atf4. (C) The ATF4-C/EBPβ complex induces PiT1 transcription in mammalian cells. NIH 3T3 cells were cotransfected with pGL3 Luc plasmid containing the –617/+825 PiT1 gene, ATF4-pcDNA3, and/or C/EBPβ-pcDNA3 expression plasmid. (D) The ATF4-C/EBPβ complex but not ATF4 or C/EBPβ alone specifically binds to the PiT1 ATF4RE. EMSA was performed using 32P-radiolabeled double-stranded oligonucleotides corresponding to the ATF4RE of the PiT1 gene. Competitive assays were performed using a 50-fold molar excess of unlabeled oligonucleotides corresponding to the WT ATF4RE or the mutant ATF4 of the PiT1 gene as indicated. Supershift assay was performed using C/EBPβ and ATF4 antibody. Black arrow: binding ATF4-C/EBPbeta complex; white arrow: supershift. (E) ATF4 and C/EBPβ belong to the same protein complex, which binds to the PiT1 ATF4RE. Double ChIP assays were performed using VSMCs incubated for 6 hours with 500 μM stearic acid that were first immunoprecipitated with ATF4 antibody, eluted, and then subjected to a second immunoprecipitation with C/EBPβ antibody or normal rabbit IgG antibody. The enrichment of ATF4-C/EBPβ protein was analyzed by real-time quantitative PCR using primer sets specific for the PiT1 ATF4RE or for the 5′ distal promoter region of PiT1 as a negative control (data not shown). Data were plotted as the percentage of antibody binding versus the amount of PCR product obtained using a standardized aliquot of input chromatin (% of input). Two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test was used for statistical analysis. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.