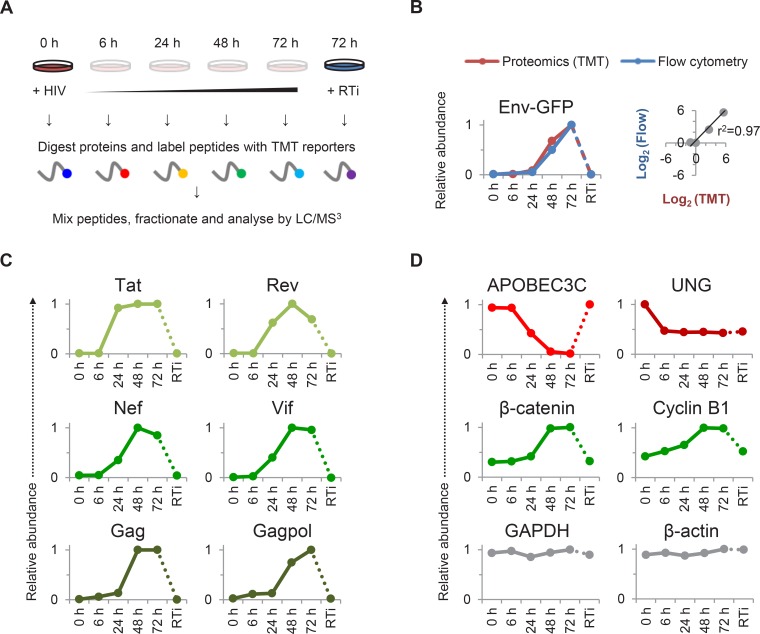
Figure 1. TMT-based proteomic time course analysis of HIV-infected cells.
(A) Workflow of 6-plex TMT-based whole cell proteomic time course experiment. CEM-T4 T cells were infected with NL4-3-dE-EGFP HIV at an MOI of 10. In subsequent figures timepoints 1–5 show protein abundance 0, 6, 24, 48 and 72 hr after HIV infection (where 0 hr = uninfected cells) and timepoint 6 shows protein abundance 72 hr after HIV infection in the presence of reverse transcriptase inhibitors (RTi). (B) Comparison of temporal profiles of Env-GFP obtained by proteomic (TMT) versus flow cytometric quantitation. Cells from (A) were analysed by flow cytometry. Relative abundance is expressed as a fraction of maximum TMT reporter ion or fluorescence intensity. For linear regression, log2 (fold change in protein abundance compared with uninfected cells) is shown. (C–D) Temporal profiles of viral proteins (C) and previously reported HIV targets (D). GAPDH and β-actin are included as controls. Relative abundance is expressed as a fraction of maximum TMT reporter ion intensity.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.18296.003