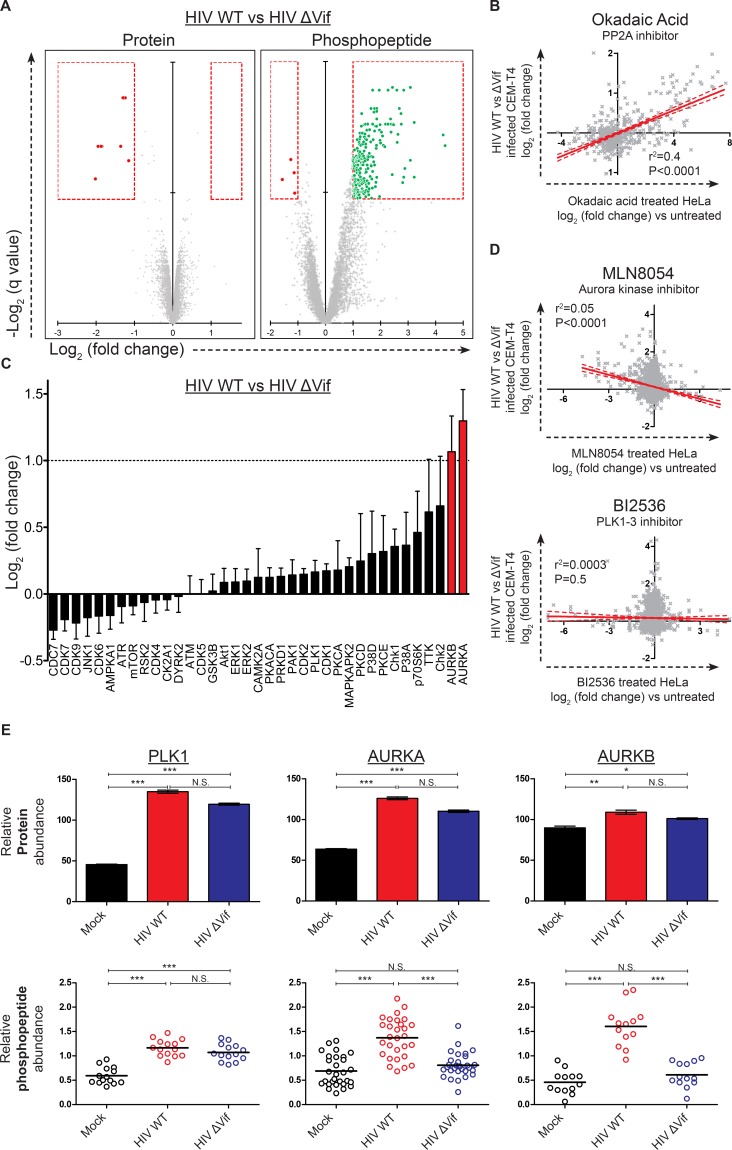
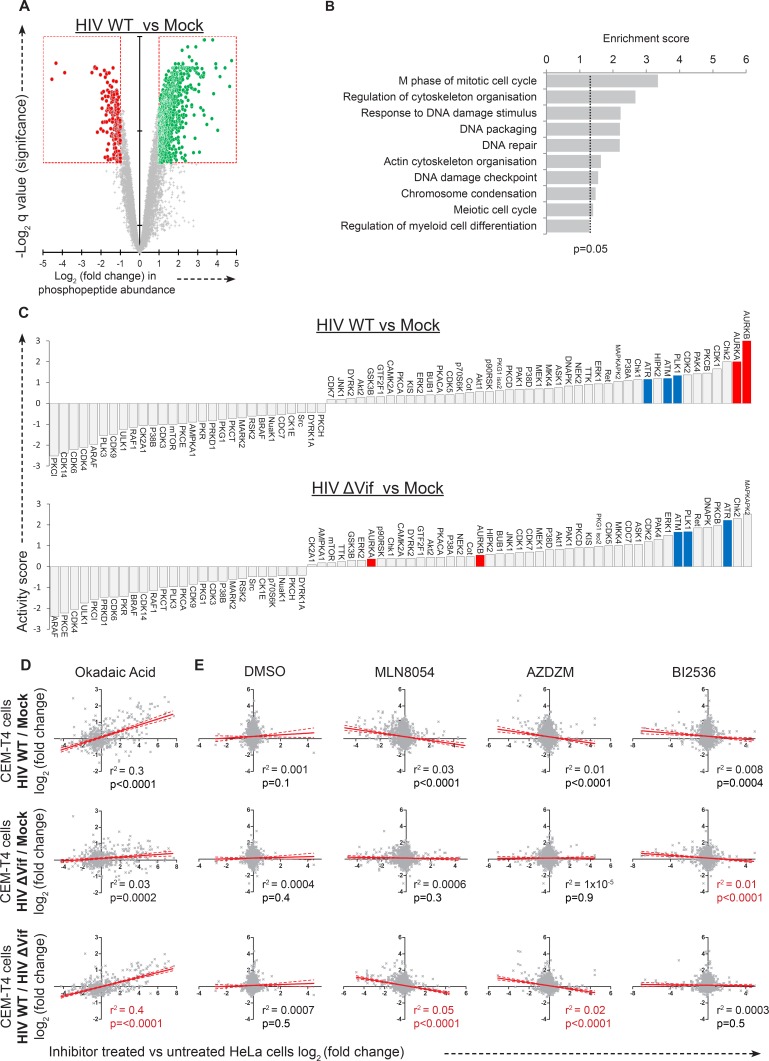
Figure 6. Global phosphoproteomic analysis of cells infected with WT or ∆Vif HIV.
(A) Vif-dependent changes in peptide and phosphopeptide abundance. CEM-T4 T cells from Figure 4A and Figure 4—figure supplement 1A were subjected to TMT-based phosphoproteomic analysis. Scatterplots display differences in protein (left panel, as in Figure 4A, right panel) and phosphopeptide abundance (right panel) between WT and ΔVif-infected cells. Each point represents a single protein or phosphopeptide, plotted by its log2 (fold change in abundance) versus the statistical significance of that change. q values were determined using Limma with Benjamini-Hochberg adjustment for multiple testing, with increasing −log2 (q value) indicating increasing significance. Proteins and phosphopeptides downregulated (red) or upregulated (green) with a fold change > 2 and q value < 0.01 are highlighted. (B) Comparison of changes in phosphopeptide abundance between WT and ΔVif-infected CEM-T4 T cells with previously published data for okadaic acid-treated HeLa cells (Kauko et al., 2015). Lines show linear correlation with associated 95% confidence areas, r2 values and p values of a non-zero correlation. (C) Analysis of changes in phosphopeptide abundance between WT and ΔVif-infected cells CEM-T4 T cells using the PhosphoSitePlus kinase-substrate database. Bars show log2 (fold change in phosphopeptide abundance) for peptides spanning known kinase substrate sites. Error bars show the standard error of the mean. (D) Comparison of changes in phosphopeptide abundance between WT and ΔVif-infected CEM-T4 T cells with previously published data for kinase inhibitor-treated HeLa cells (Kettenbach et al., 2011). At low concentrations, MLN8054 is a selective AURKA inhibitor, but at 5 μM (as shown) reduced activity of AURKB and PLK1 is also observed. Lines show linear correlation with associated 95% confidence areas, r2 values and p values of a non-zero correlation. (E) Vif-specific hyperphosphorylation of aurora kinase substrates. Protein abundances of PLK1, AURKA and AURKB were compared with normalised abundances of manually curated phosphopeptides targeted by the respective kinases. Abundances of kinase proteins were compared using Limma with Benjamini-Hochberg adjustment for multiple testing. Abundances of target phosphopeptides were compared by Repeated Measures ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test. N.S., p value>0.05; *p value<0.05; **p value<0.01; ***p value<0.001.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.18296.019