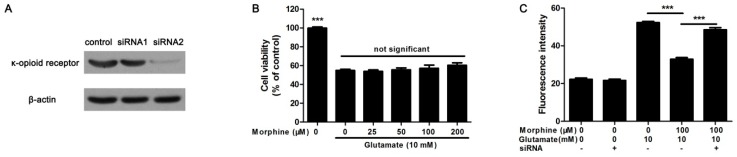
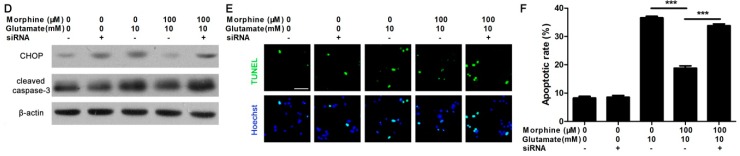
Figure 4.
Knockdown κ-receptor reduces the protective effect of morphine on glutamate-treated astrocytes. (A) To detect the knockdown efficacy of two different siRNAs, the expression of κ-receptor was detected by western blot after the cells were treated with siRNAs, β-actin was internal control; (B) following 24 h treatment, cell viability in κ-opioid receptor knockdown astrocytes was determined by MTT assay, *** p < 0.001 compared to glutamate only treated group, n = 6; (C) glutamate-initiated calcium release in κ-opioid receptor knockdown astrocytes was determined by fluorescence microplate. *** p < 0.001 indicated significances, n = 6; (D) following 24 h treatment, the cells were lysed and the protein was extracted to detect the expression of CHOP and cleaved caspase-3, β-actin was internal control, blots were representative of three independent experiments; (E) following 24 h treatment, the cells were fixed and TUNEL staining was performed to detect apoptotic cells. Green fluorescence was TUNEL-positive nuclei, blue fluorescence was all nuclei stained by Hoechst 33342, scale bar = 50 μm and referred to all panels; (F) apoptotic rate was calculated as TUNEL-positive nuclei divided by total nuclei, *** p < 0.001 indicated significances, n = 15.