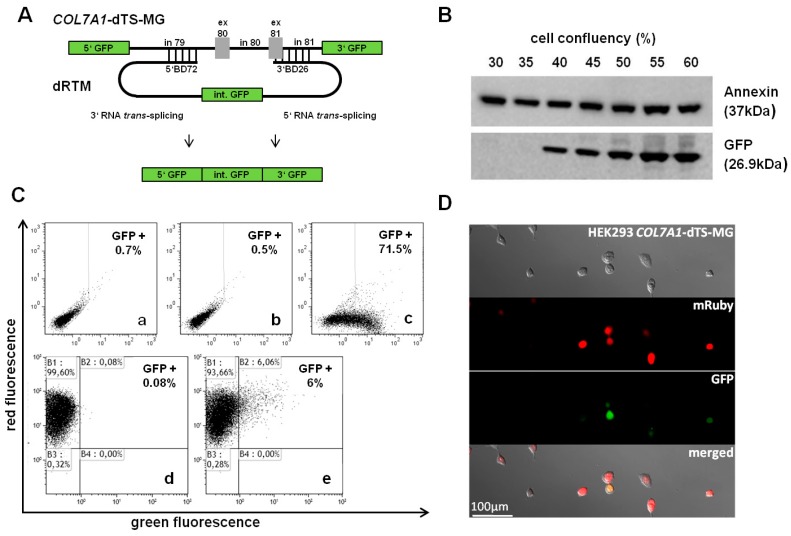
Figure 2.
Fluorescence-based simulation of replacement of internal COL7A1 exons. (A) Schematic depiction of GFP-based RTM analysis system. COL7A1-dTS-MG contains the 5′ and 3′ end of GFP flanking the COL7A1 gene sequence intron 79–intron 81. dRTM-GFP comprises two binding domains specific for intron 79 and exon/intron 81, respectively, two splicing domains and the internal GFP part to be introduced into the target minigene. Accurate 5′ and 3′ trans-splicing between the COL7A1-dTS-MG and the dRTM-GFP leads to the fusion of the three individual GFP parts resulting in the expression of full-length GFP; (B) Restored full-length GFP was detectable at protein level by Western blot analysis of total cell extracts of HEK293 cells co-transfected with COL7A1-dTS-MG and dRTM-GFP. Annexin I was included as loading control; (C) Flow cytometric analysis of HEK293 cells transfected with COL7A1-dTS-MG (a), dRTM-GFP (b) or both: COL7A1-dTS-MG and dRTM-GFP (c) restoring GFP in up to 71% of all treated cells. HEK293 cells stably expressing the COL7A1-dTS-MG do not show GFP expression (d), whereas dRTM-GFP transfection leads to expression of GFP upon correct double RNA trans-splicing in up to 6% of all analysed cells (e). The FACS gates were set on the negative control, consisting of exclusively COL7A1-dTS-MG transfected HEK293 cells (a); (D) Microscopic analysis of HEK293 cells stably expressing COL7A1-dTS-MG and the red fluorescence reporter mRuby revealed the restoration of GFP expression pattern after dRTM introduction. GFP: green fluorescent protein; ex: exon; in: intron; BD: binding domain; int.: internal.