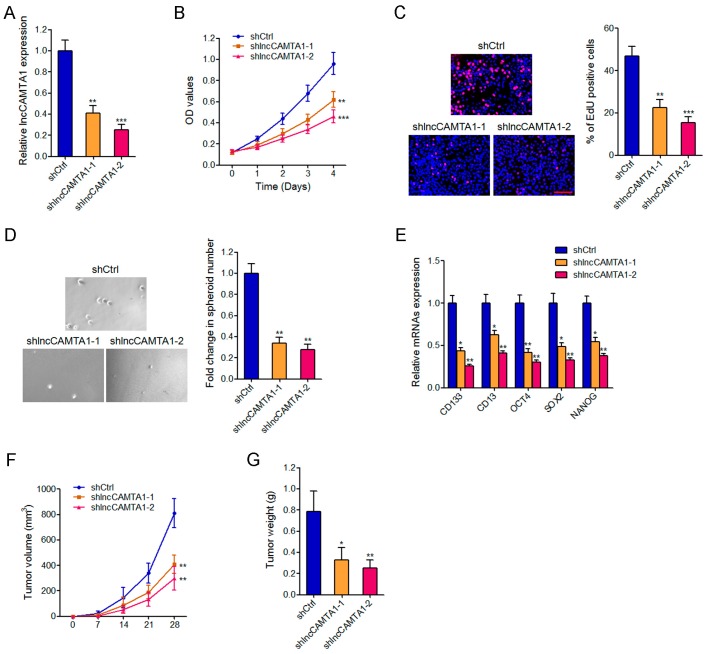
Figure 5.
Depletion of lncCAMTA1 inhibits HCC cell proliferation, CSC-like properties, and tumorigenesis. (A) lncCAMTA1 expression in lncCAMTA1 stably depleted and control HepG2 cells; (B) Cell proliferation of lncCAMTA1 stably depleted and control HepG2 cells was detected by CCK-8 assay, and the relative number of cells compared to day 0 is presented; (C) Cell proliferation of lncCAMTA1 stably depleted and control HepG2 cells was detected by EdU incorporation assays. Scale bar = 100 μm; (D) Spheroid formation assays showed that knockdown of lncCAMTA1 decreased the number of spheroids generated from HepG2 cells; (E) Depletion of lncCAMTA1 downregulated the expression of stem cell markers and transcription factors CD133, CD13, OCT4, SOX2, and NANOG. For A–E, data are shown as mean ± SD. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 by Student’s t test; (F,G) Depletion of lncCAMTA1 inhibited in vivo tumor growth of HepG2 cells. lncCAMTA1 stably depleted and control HepG2 cells were subcutaneously injected into nude mice. Tumor volumes were measured every 7 days (F), and tumor weights were measured at 28 days after injection (G). n = 6 mice in each group, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 by Mann–Whitney test.