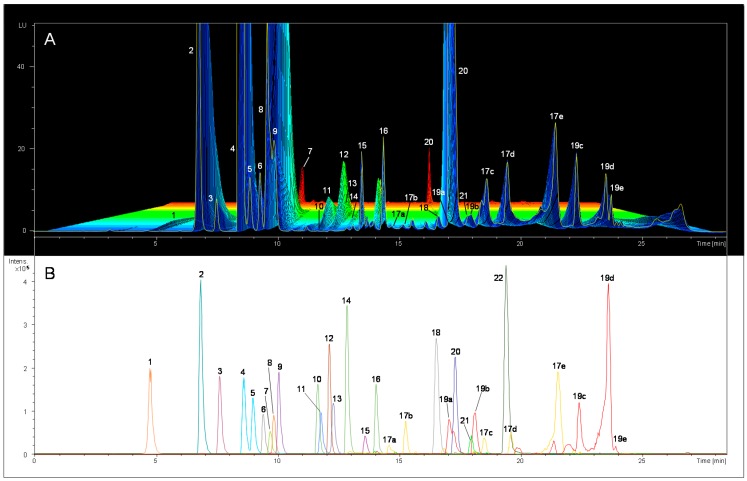
Figure 1.
(A) 3D-plot of a fortified extra-VOO extract with eighteen phenolic compounds at a final concentration level of 10 μg·mL−1, when excitation wavelength is set at 285 nm and the zero order emission spectra is recorded; (B) Extracted ion chromatograms (EICs) of the known phenolic compounds for the same fortified extract as in (A), obtained in electrospray ionization–ion trap MS (ESI-IT MS) detector (using negative ionization mode). Peak identification numbers: (1) Gallic acid (Gal); (2) HTY; (3) 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC) (used as internal standard (IS)); (4) TY; (5) 4-hydroxybenzoic acid (4-HBA); (6) 4-hydroxyphenylacetic (4-HPA); (7) vanillic acid (Van); (8) syringic acid (Syr); (9) homovanillic acid (Hmvan); (10) p-coumaric acid (p-Cou); (11) vanillin (Val); (12) sinapic acid (Sin); (13) ferulic acid (Fer); (14) m-coumaric acid (m-Cou); (15) oleuropein (Ole); (16) o-coumaric acid (o-Cou); (17) oleuropein aglycon (OleAgly) and isomers; (18) luteolin (Lut); (19) ligstroside aglycon (LigAgly) and isomers; (20) (+)-pinoresinol (Pin); (21) acetoxypinoresinol (AcPin); and (22) Apig. As far as the different isomers of OleAgly and LigAgly are concerned, they are identified by adding a letter (a–e) to the number assigned for the main isomer.