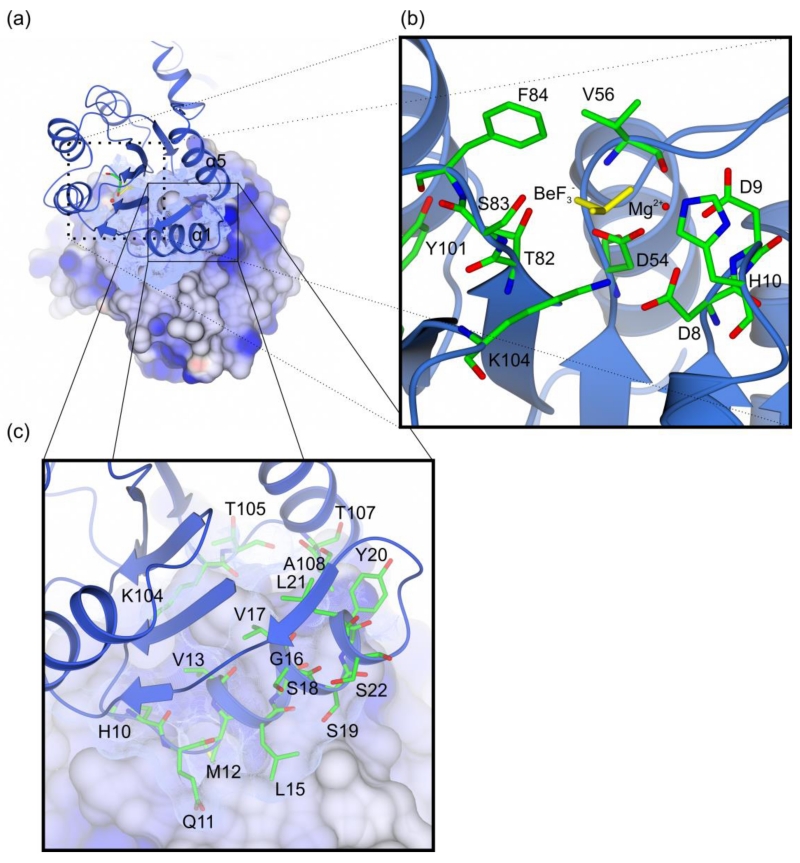
Figure 3. Overview of the LiaR receiver domain dimer.
(a) The receiver domain forms a dimer through a hydrophobic interface of 692 Å2 that juxtaposes the α1 and α5 helices of two LiaR protomers; (b) LiaR active site in the presence of BeF3− (yellow) and Mg2+ (red). The residues Thr83 and Tyr102, adopt a characteristic active conformation, toward the predicted phosphorylation site at Asp54. BeF3− is also in a position to make hydrogen bonds to Thr82 and Ser83 and a salt bridge to Lys104; (c) Key residues are shown that comprise the dimerization interface in a manner comparable to that observed for VraR. Met12 from one protomer docks into a hydrophobic pocket within the dimerization interface of the second LiaR protomer.