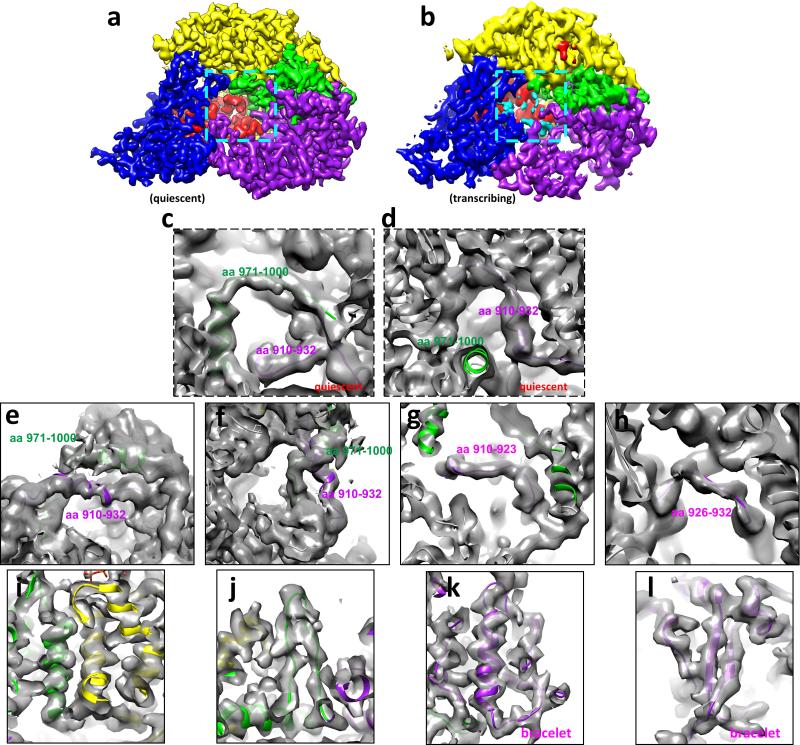
Extended Data Figure 8. Tracing amino acid residues 910-932 and 971-1000 of module B of the bracelet domain of RdRP in the quiescent and transcribing states.
a-b, CryoEM densities of RdRP in the quiescent (a) and transcribing (b) states. The locations of the residues 910-932 and 971-1000 are indicated with cyan boxes in (a) and (b). Due to their flexibility, these residues are not readily visible when displayed as in (a) and (b) but become visible when the maps are filtered to a lower resolution (e.g., 4.5Å resolution) as in (c-f). The colour scheme of domains/subdomains is the same as in Figure 3a. c, Trace of the residues 971-1000 (green) and 910-932 (purple) of module B of the bracelet domain of RdRP in the quiescent state. d, The same as (c) but in a different view. e, Trace of the residues 971-1000 (green) and 910-932 (purple) of module B of the bracelet domain of RdRP in the transcribing state. f, The same as (e) but in a different view to show the unambiguous trace of the two peptide fragments. g-h, Trace of the residues 910-923 (g) (purple) and 926-932 (h) (purple) of the bracelet domain of RdRP in the transcribing state, showing the unambiguous trace of the two peptide fragments. i-j, CryoEM densities (grey) and model (ribbon) of RdRP in the transcribing state, showing α-helices (i) and a β-hairpin (j). The colour scheme of domains/subdomains is the same as in Figure 3a. k-l, Trace of the residues of the bracelet domain of RdRP in the transcribing state, showing a α-helix (k) and a β-sheet (l).