Figure 1.
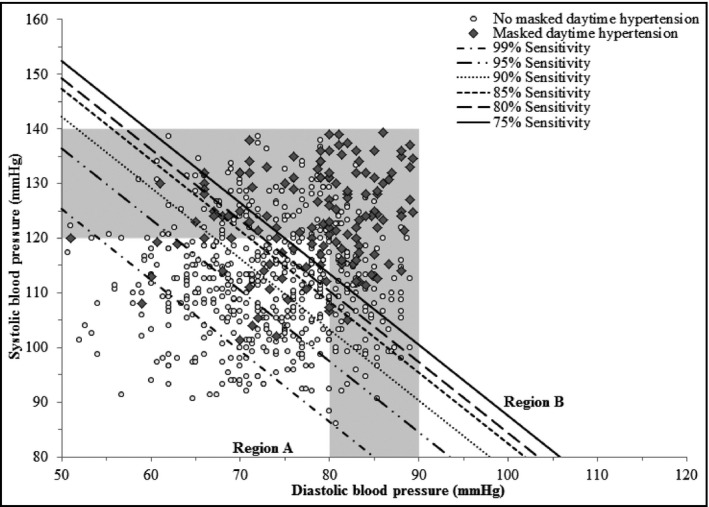
Scatterplot of clinic systolic vs diastolic blood pressure demonstrating derived cut points corresponding with specified sensitivity levels for detecting masked daytime hypertension using the clinic blood pressure index equation in the pooled validation cohort of participants in the Improving the Detection of Hypertension Study and Jackson Heart Study (n=675). The shaded region represents the clinic blood pressure values corresponding with prehypertension defined as systolic blood pressure ≥120 mm Hg and <140 mm Hg and/or diastolic blood pressure ≥80 mm Hg and <90 mm Hg. Region A: The clinic blood pressure diagnostic index, defined as systolic clinic blood pressure + 1.3*diastolic clinic blood pressure, was categorized as normal (ie, below the cut point corresponding with the specified sensitivity level). Region B: The clinic blood pressure diagnostic index, defined as systolic clinic blood pressure + 1.3*diastolic clinic blood pressure, was categorized as elevated (ie, at or above the cut point corresponding with the specified sensitivity level). Cut points for an elevated clinic blood pressure diagnostic index corresponding with the specified sensitivity levels are: sensitivity 99%: ≥190 mm Hg; sensitivity 95%: ≥201 mm Hg; sensitivity 90%: ≥207 mm Hg; sensitivity 85%: ≥212 mm Hg; sensitivity 80%: ≥214 mm Hg; and sensitivity 75%: ≥217 mm Hg.
