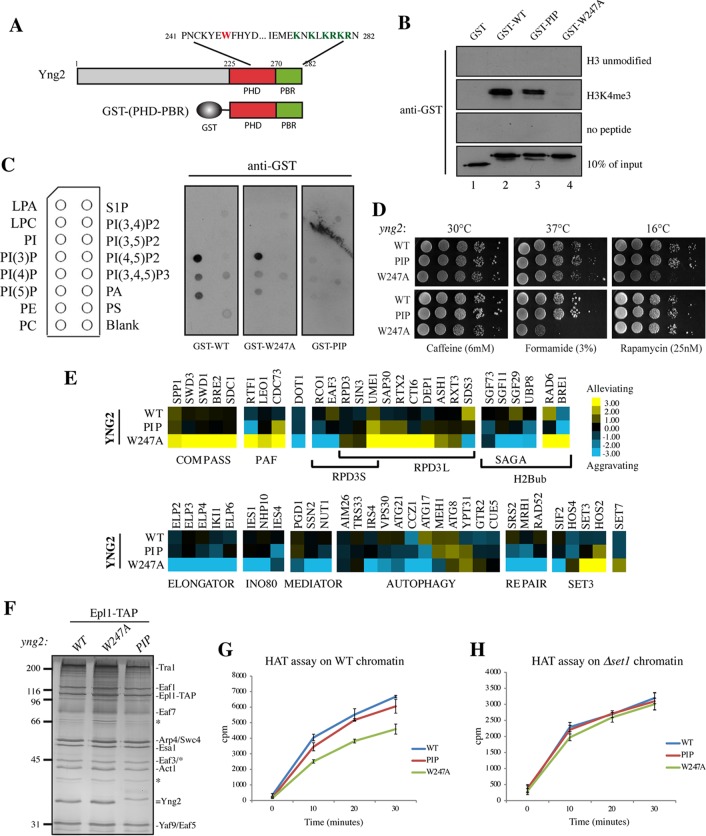
FIG 3.
The Yng2 C terminus contains two functionally distinct domains, PHD and PBR. (A) Schematic representation of the Yng2 PHD and PIP-binding domains depicting the amino acid sequence with mutated W247 in the PHD (red) and the 6K/R mutated in the PBR (green), corresponding to K274, K276, K278, R279, K280, and R282. The GST-(PHD-PBR) construction used in the in vitro assays whose results are presented in panels B and C is also schematically represented. (B) Peptide pulldown assay of purified GST-Yng2 WT or the 6K/R-A (designated PIP) or W247A mutant with H3K4me3 and unmodified H3 peptides. Specific binding was detected by Western blotting using an anti-GST antibody. (Note that the slightly less apparent binding of the PIP mutant is explained by the smaller amount of input protein.) (C) Lipid dot blots were probed with purified GST-Yng2-(PHD-PBR) WT or the W247A or PIP mutant, as indicated, and specific binding to lipids was detected with an anti-GST antibody. A schematic representation of the overlay is given on the left, and the definitions of the abbreviations are as follows: LPA, lysophosphatidic acid; LPC, lysophosphatidylcholine; PI, phosphatidylinositol; PI(3)P, phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate; PI(4)P, phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate; PI(5)P, phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PC, phosphatidylcholine. (D) Spot assays showing the effect of PIP and W247A mutations on cell growth. Tenfold serial dilutions of the indicated cells were grown for 2 to 10 days on YPD at either 30°C, 37°C, or 16°C (top) or at 30°C on the indicated drug-containing medium (bottom). (E) Subsets of genetic interaction profiles for WT and the yng2-PIP and yng2-W247A mutants. Blue and yellow represent aggravating and alleviating genetic interactions, respectively (i.e., slower or faster growth/fitness compared to the baseline expected from the accumulation of the individual effects of the single mutations). Strong positive genetic interactions between the yng2-W247A mutant and subunits of the COMPASS or PAF complex and strong negative interactions with subunits of Elongator or INO80 factors were observed, while genetic interactions of these factors with the yng2-PIP mutant were rare and only moderate. (F) Silver-stained gel of NuA4 complexes purified from WT cells and yng2-W247A and yng2-PIP mutant cells and used in the HAT assays. Note the similar level of Yng2 protein in wild-type and mutant complexes and the shift in migration of the PIP mutant because of the loss of a positive charge. Molecular size markers (in kilodaltons) are indicated on the left, and bands corresponding to subunits are identified on the right. (G and H) Kinetics of acetylation by the NuA4 complexes shown in panel F on native chromatin purified from WT (G) and Δset1 mutant (H) cells. After 15 min of preincubation at room temperature of complexes with the substrate, the reactions were stopped at the indicated times and processed as described in the legend to Fig. 2. NuA4 complexes were normalized according to their HAT activity on free histones purified from HeLa cells.