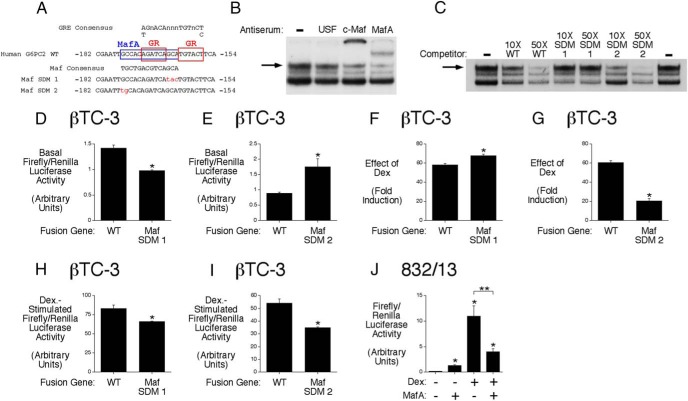
Figure 1.
The GR stimulates G6PC2 promoter activity by displacing MafA. A, The G6PC2 GRE overlaps a binding site for MafA (24). B, Gel retardation supershift assays demonstrate that MafA binds the −182/−154 G6PC2 promoter region. The c-Maf antiserum cross-reacts with MafA (13). A representative gel is shown. C, Gel retardation competition experiments demonstrate that the order of MafA-binding affinity to the sequences shown in A is Maf SDM 2 > WT > Maf SDM 1. A representative gel is shown. D–I, Effect of promoter mutations on basal and Dex-stimulated G6PC2-luciferase fusion gene expression in βTC-3 cells. A reduction in MafA binding (Maf SDM 1) decreases basal expression but has variable effects on the Dex response. An increase in MafA binding (Maf SDM 2) increases basal expression and consistently reduces the Dex response. Results show the mean ± SEM of 3 experiments; *, P < .05 vs control. J, Effect of MafA overexpression on Dex-stimulated G6PC2-luciferase fusion gene expression in 832/13 cells. Overexpression of MafA inhibits G6PC2-luciferase fusion gene expression. Results show the mean ± SEM of 3 experiments; *, P < .05 vs control.