FIG 3.
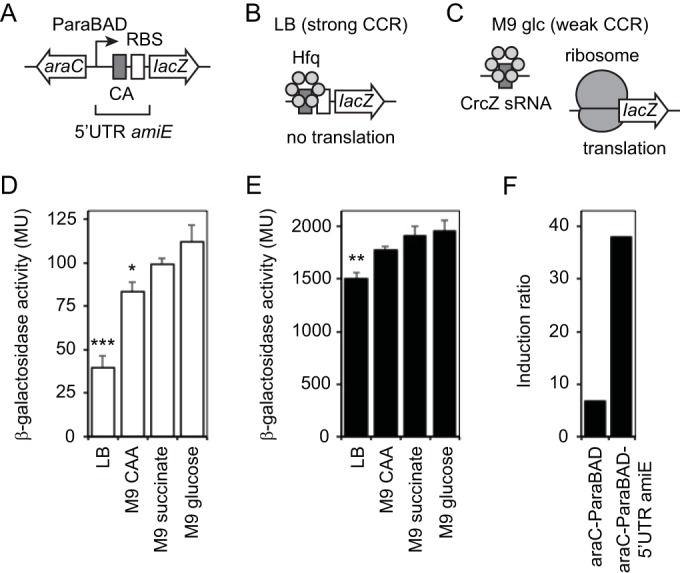
5′ UTR of P. aeruginosa amiE decreased noninduced expression from araC-ParaBAD through carbon catabolite repression. (A) Design of araC-ParaBAD inducible promoter system with 5′ UTR of P. aeruginosa amiE and lacZ reporter. (B) Inhibition of lacZ mRNA translation by strong carbon catabolite repression (CCR) in LB medium. Hfq binds CA motif in 5′ UTR amiE and blocks formation of translation initiation complex. (C) Translation of lacZ mRNA under weak carbon catabolite repression (CCR) in M9 glucose. CrcZ sRNA sequesters Hfq and allows formation of translation initiation complex. (D) PA103 attTn7::araC-ParaBAD-5′ UTR amiE-lacZ frt strain was grown to mid-exponential growth phase in LB, M9–0.5% Casamino Acids (CAA), M9–50 mM succinate, and M9–0.5% glucose without arabinose. β-Galactosidase activity was measured. Statistical significance was determined using one-way analysis of variance followed by Dunnett's test comparing each to M9 glucose (*, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001). (E) Cells were grown to mid-exponential growth phase with 0.8% arabinose in LB, M9–0.5% Casamino Acids (CAA), M9–50 mM succinate, and M9–0.5% glucose. Statistical significance was determined as described above. (F) Comparison of induction ratios without 5′ UTR amiE and with 5′ UTR amiE in LB. Induction ratio is maximum induced activity to noninduced activity.
