Figure 2.
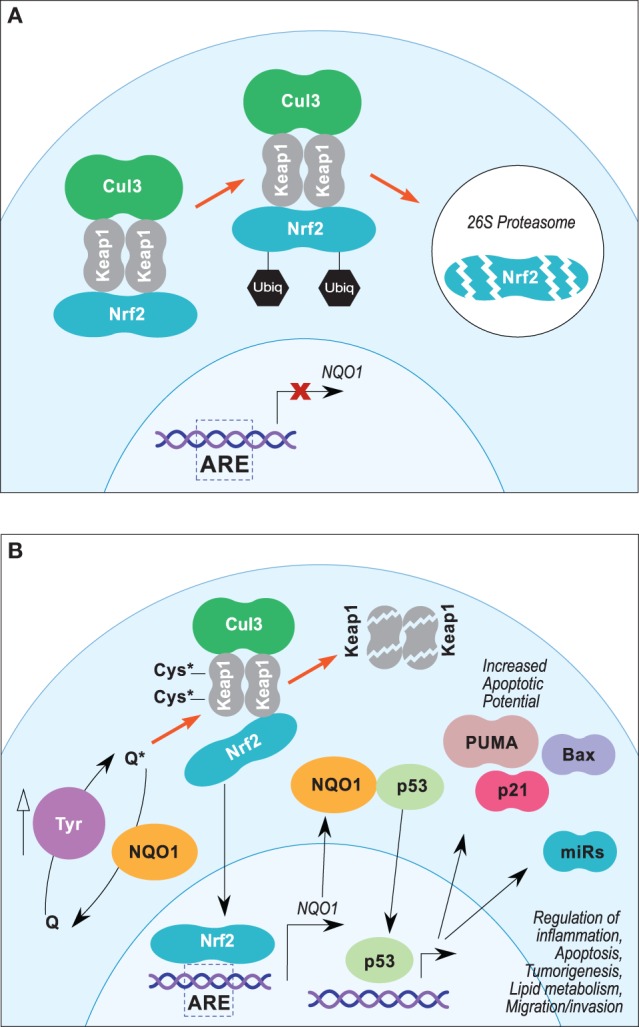
(A,B) Proposed Nrf2/ARE pathway leading to NQO1-mediated p53 stabilization in melanoma. (A) In steady-state conditions, Nrf2 transcriptional activity is suppressed by Keap1, which sequesters Nrf2 in the cytosol and facilitates Cul3-dependent ubiquitinylation and 26S proteasomal degradation. (B) Electrophilic stress at key cysteine residues of Keap1 leads to disassociation of Keap1/NRF2–DLG interface, which inhibits Cul3-dependent ubiquitinylation and promotes Keap1 degradation. Degradation of Keap1 protein allows accumulation of Nrf2 and translocation into the nucleus, which promotes expression of NQO1 and other genes under the control of AREs. Stabilization of p53 by NQO1 may potentiate expression of proapoptotic proteins and miRNAs.
