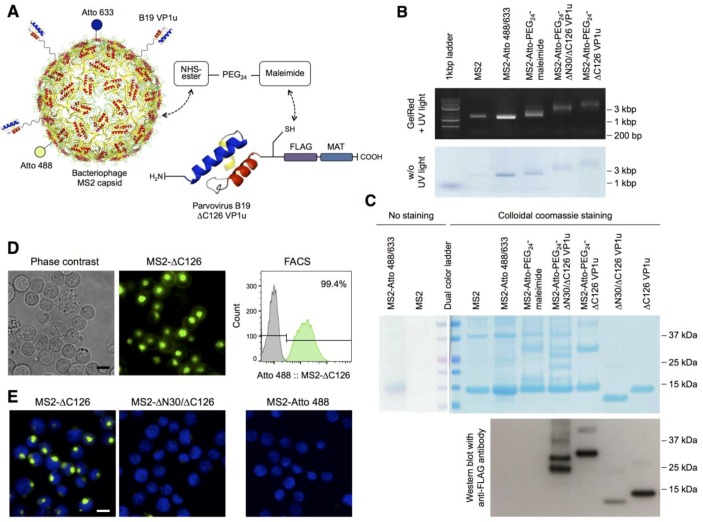
Figure 1.
Bioconjugation of the B19 viral protein 1 unique region (VP1u) with the bacteriophage MS2 capsid, and internalization of the bioconjugate on erythroleukemic UT7/Epo cells: (A) Schematic depiction of the bioconjugation and labeling strategy of the bacteriophage MS2 capsid (PDB ID: 1MST [28]). The recombinant ∆C126 VP1u protein with a C-terminal metal affinity tag (MAT), FLAG tag, and a unique cysteine was coupled to the MS2 capsid using the heterobifunctional maleimide-PEG24-N-hydroxysuccinimide ester (NHS-PEG24-maleimide) crosslinker. The NHS-ester was conjugated to the surface lysines of the MS2 capsid and the maleimide group reacted with the unique cysteine in the VP1u. In addition, the capsid was labeled with the NHS-Atto 488 (green) and NHS-Atto 633 (blue) dyes; (B) Migration of the wild-type (WT) and bioconjugated MS2 capsids by agarose gel electrophoresis and detection of encapsidated RNA with GelRed. Capsid proteins are labeled with NHS-Atto dyes (green-blue); (C) Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and Western blot analysis of the MS2 capsids, recombinant VP1u proteins, and the bioconjugates. Recombinant VP1u and MS2-VP1u conjugates were detected with an anti-FLAG antibody. In the Western blot, the transfer of low molecular weights proteins was less efficient; therefore, the detected signal did not quantitatively reflect the original and relative input of the proteins; (D) Uptake of the fluorescent MS2-∆C126 VP1u into UT7/Epo cells and detection of the internalized capsids in living cells by fluorescence microscopy and fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS); (E) Fluorescence microscopy images of the MS2-∆C126 VP1u and the Atto-labeled but internalization-deficient controls MS2-∆N30/∆C126 VP1u and MS2 (63× magnification). Scale bar: 15 µm.