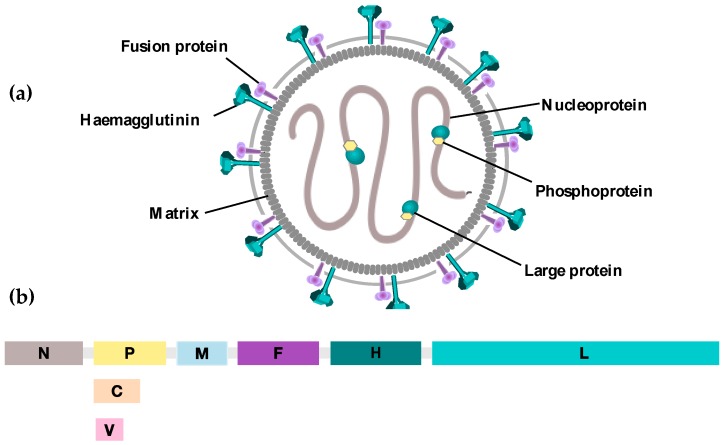
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of (a) measles virus. Measles virus is an enveloped negative strand RNA virus. The RNA genome is protected by nucleoproteins (N) which are associated with a RNA dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), known as Large Protein (L), and its cofactor Phosphoprotein (P). Together these comprise the ribonucleoprotein complex (RNP) that is surrounded by the matrix (M). The two viral glycoproteins, Haemagglutinin (H) protein and the Fusion (F) protein, project from the lipid bilayer and are involved in viral entry to the host cell; (b) Measles virus genome. The MV genome consists of 15,894 RNA nucleotides comprising six transcription units each separated by trinuclear intergenic sequences. A transcriptional gradient is generated whereby mRNAs are generated with decreasing abundance from the 3′ N to the 5′ L position. The proteins V and C are non-structural proteins that are generated from an alternative RNA transcript of the P gene.