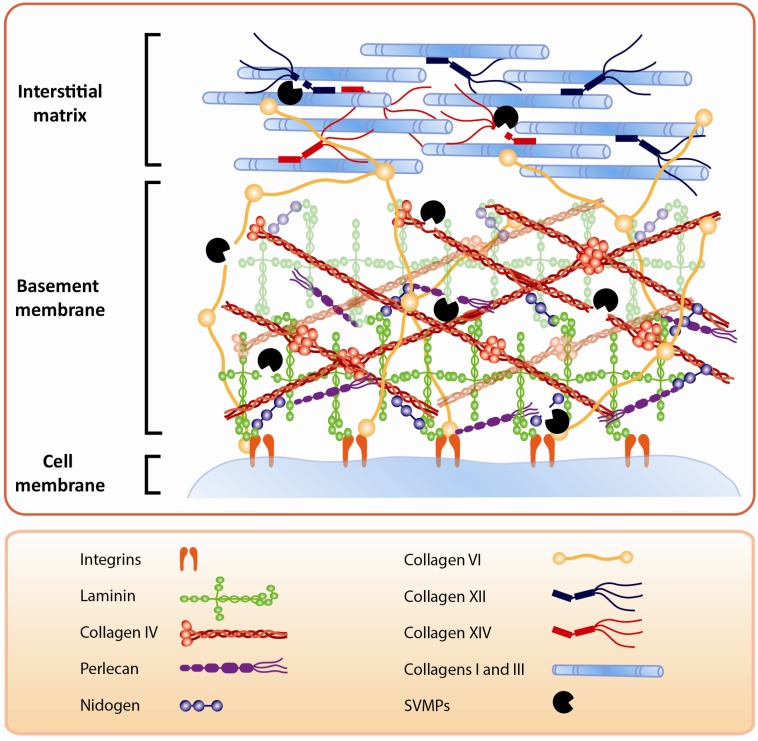
Figure 4.
Hydrolysis of ECM components by SVMPs. Some SVMPs hydrolyze components at the BM of capillary vessels, skeletal muscle fibers, and dermal-epidermal junction. In the case of hemorrhagic SVMPs, it has been postulated that hydrolysis of type IV collagen is a key step in the destabilization of BM, which leads to extravasation. SVMPs also hydrolyze additional ECM proteins, such as FACITs, type VI collagen, and other components that connect the BM with the surrounding matrix stromal proteins. Moreover, SVMP degrade proteins that bind to and organize fibrillar collagens, leading to a disorganization of the ECM supramolecular structure. SVMPs may also hydrolyze plasma membrane components, such as integrins, that interact with BM components. All these hydrolytic actions result in a profound alteration of ECM, with consequences for the processes of venom-induced tissue damage, repair, and regeneration.