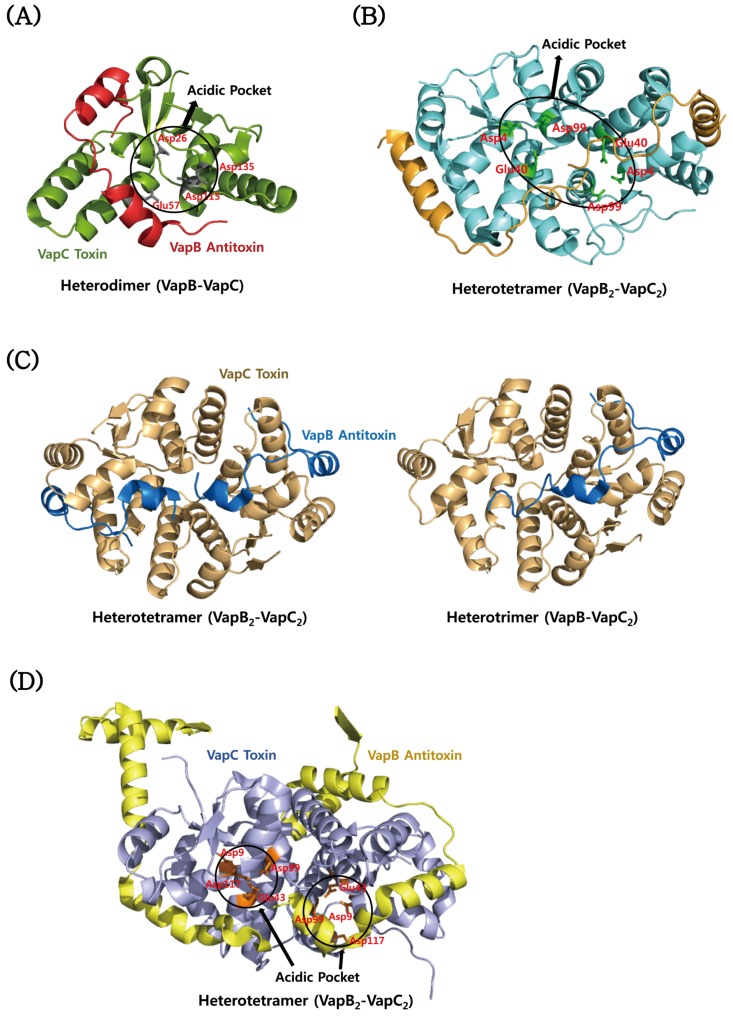
Figure 4.
Structural comparisons of VapBC proteins from M. tuberculosis. (A) Structure of the VapBC complex (Rv0626–Rv0627). Four conserved residues of VapC are clustered to form an acidic pocket. (B) Structure of the VapBC complex (Rv0623–Rv0624). Three conserved acidic residues of each VapC subunit are positioned in the dimeric interface of VapC. (C) Structure of the VapBC complex (Rv2009–Rv2010). VapC dimers bind to one and two VapB with a stoichiometry of 2:1 and 2:2, respectively. (D) Structure of the VapBC complex (Rv0300–Rv0301). Four conserved residues of each VapC monomer are clustered to form an acidic pocket.