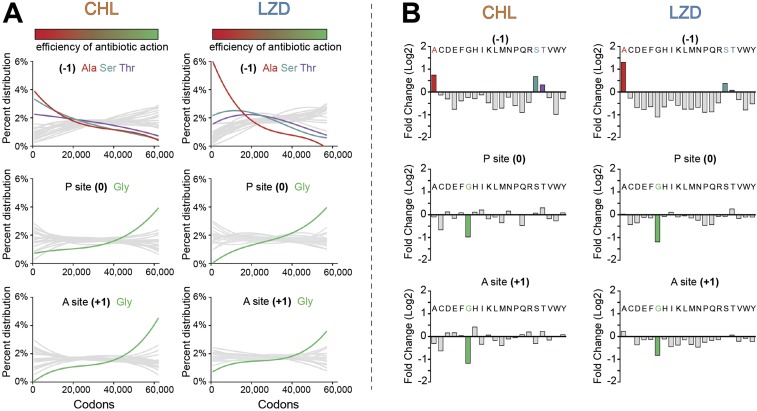
Fig. S5.
The efficiency of CHL- or LZD-induced translation arrest correlates with the presence of Ala, Ser, or Thr in the penultimate position of the nascent chain and countercorrelates with the presence of Gly in the P or A site. (A, graphs at Top) Occurrence of Ala, Ser, or Thr in the penultimate position (−1) of the nascent chain along the spectrum of the analyzed sites arranged according to the efficiency of antibiotic action (see SI Materials and Methods for detail). (Middle and Bottom) Occurrence of Gly in the P site (position 0) (Middle) or A site (position +1) (Bottom) of the drug-stalled ribosome. The colored bars at the Top mark all of the analyzed sites arranged as in Fig. 2 in the main text according to the efficiency of antibiotic action: from the sites of the strongest drug-induced arrest on the Left (red) to the sites of the least pronounced arrest on the Right (green). (B) Analysis of the cumulative drug-induced changes in the ribosome density at all of the analyzed sites according to the nature of amino acid in the penultimate position (−1) of the nascent chain (Top), P site (0) (Middle), or A site (+1) (Bottom).