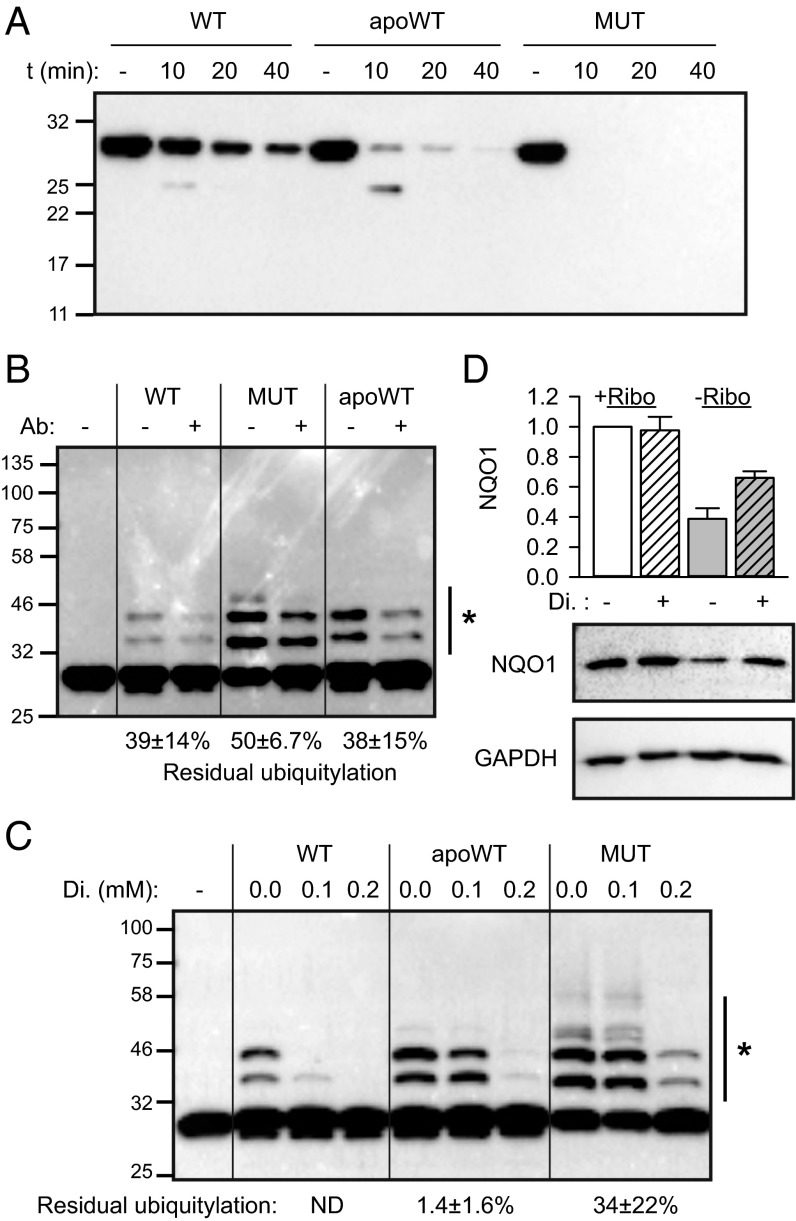
Fig. 3.
The C-terminus sensitizes NQO1 to recognition by CHIP. (A) Hydrolysis of the protruding C-terminus of wild-type NQO1, apoNQO1 (apoWT), and the P187S mutant (MUT) using trypsin. Hydrolysis time (t) is indicated. Anti-NQO1 antibody recognizing the last 12 amino acids of the protein was used. One representative experiment of three is shown. (B) Residual ubiquitylation of different forms of NQO1 in the presence of the C-terminus of NQO1-recognizing antibody was analyzed and is indicated (n = 3, mean ± SD). The side bar with an asterisk indicates the bands used for quantification. Ubiquitylation without added antibody was set as 100%. (C) Residual ubiquitylation of different forms of NQO1 in the presence of the indicated concentrations of dicoumarol (Di.) was analyzed. The side bar with an asterisk indicates the bands used for quantification. Ubiquitylation without added dicoumarol was set as 100%; residual ubiquitylation at 0.2 mM dicoumarol is indicated (n = 3, mean ± SD). (D) Rescue of apoNQO1 in riboflavin-free medium (−Ribo) by dicoumarol (n = 3, mean ± SD). Hatched bars represent samples treated with 100 μM dicoumarol for 24 h.