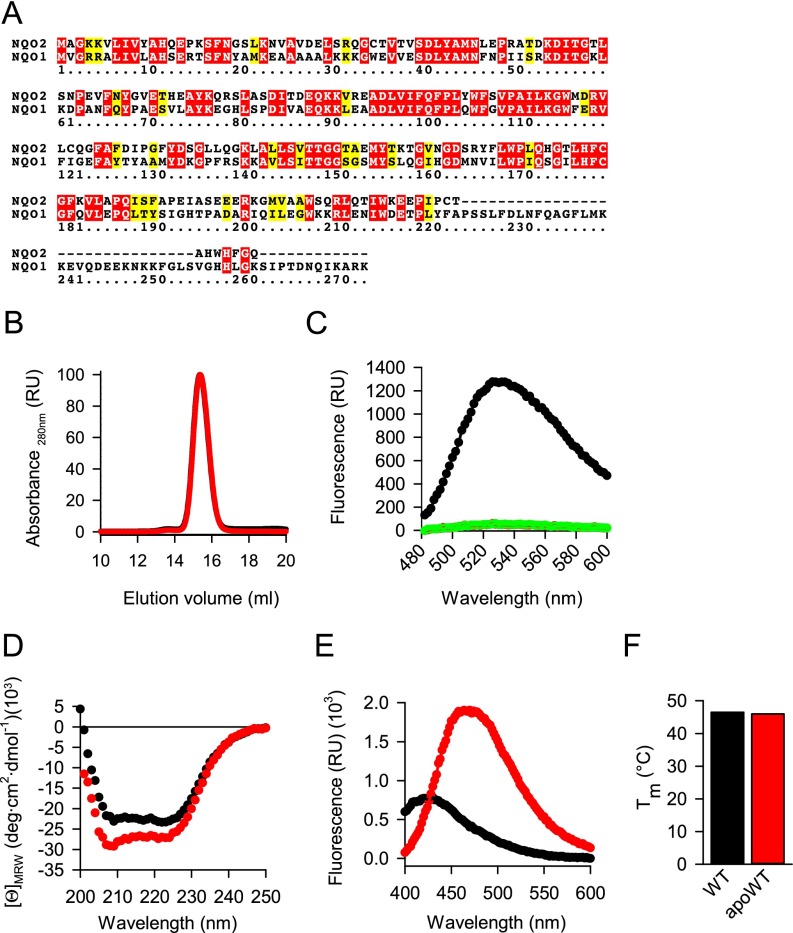
Fig. S5.
Preparation and characterization of cofactor-free NQO2. (A) Sequences of human NQO1 (UniProt ID 15559) and NQO2 (UniProt ID P16083) were aligned using the CLUSTALW algorithm. Identical amino acids are in red; similar amino acids are in yellow. (B) Gel filtration of wild-type NQO2 (black trace, covered by the red trace) and apoprotein (red trace). The maximum absorbance at 280 nm was set as 100. The absorbance of eluting proteins is shown. (C) Wild-type NQO2 (black trace) and apoprotein (red trace, covered by the green trace) were processed, and the fluorescence of the released FAD was measured as detailed in SI Materials and Methods. FAD (1,000 nM) was included as a positive control (green trace). (D–F) Biophysical analyses of wild-type NQO2 (black traces) and apoprotein NQO2 (apoWT; red traces). (D) CD spectroscopy. Average values from three independent measurements are plotted. (E) ANS binding. One representative of three independent measurements is plotted. (F) Melting of the indicated protein was measured using a fluorescent melting assay. The average melting temperature is plotted (n = 3, mean ± SD).